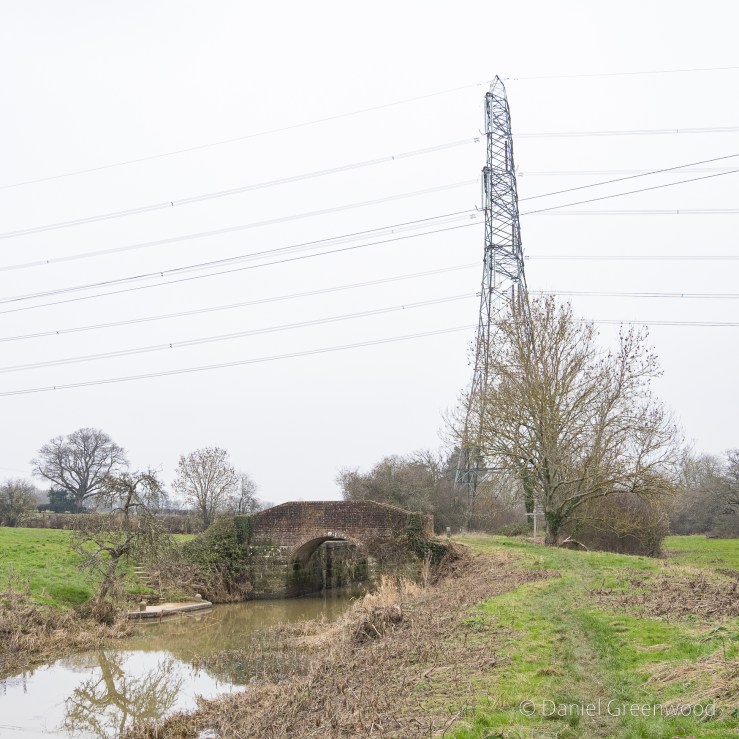
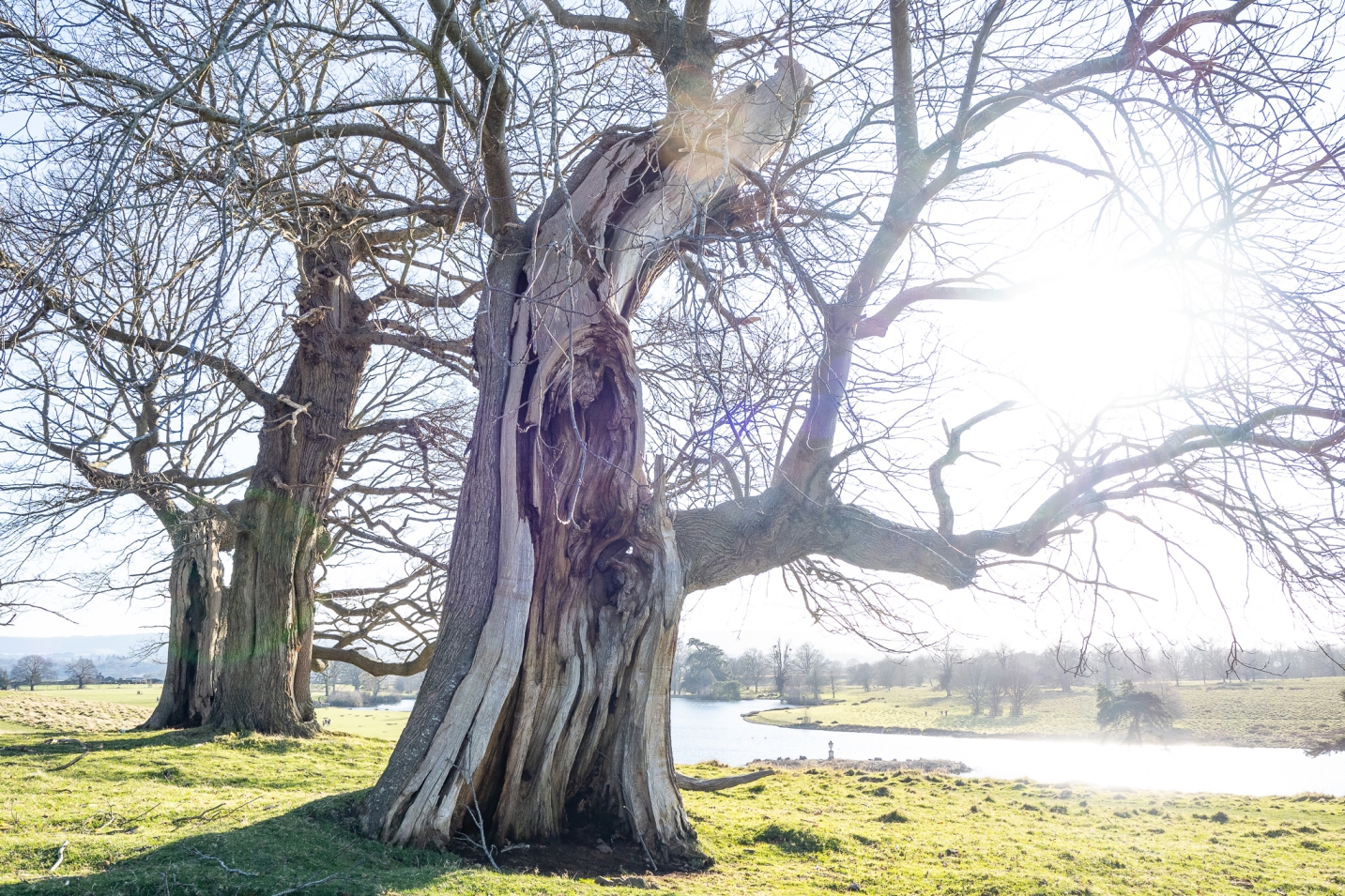
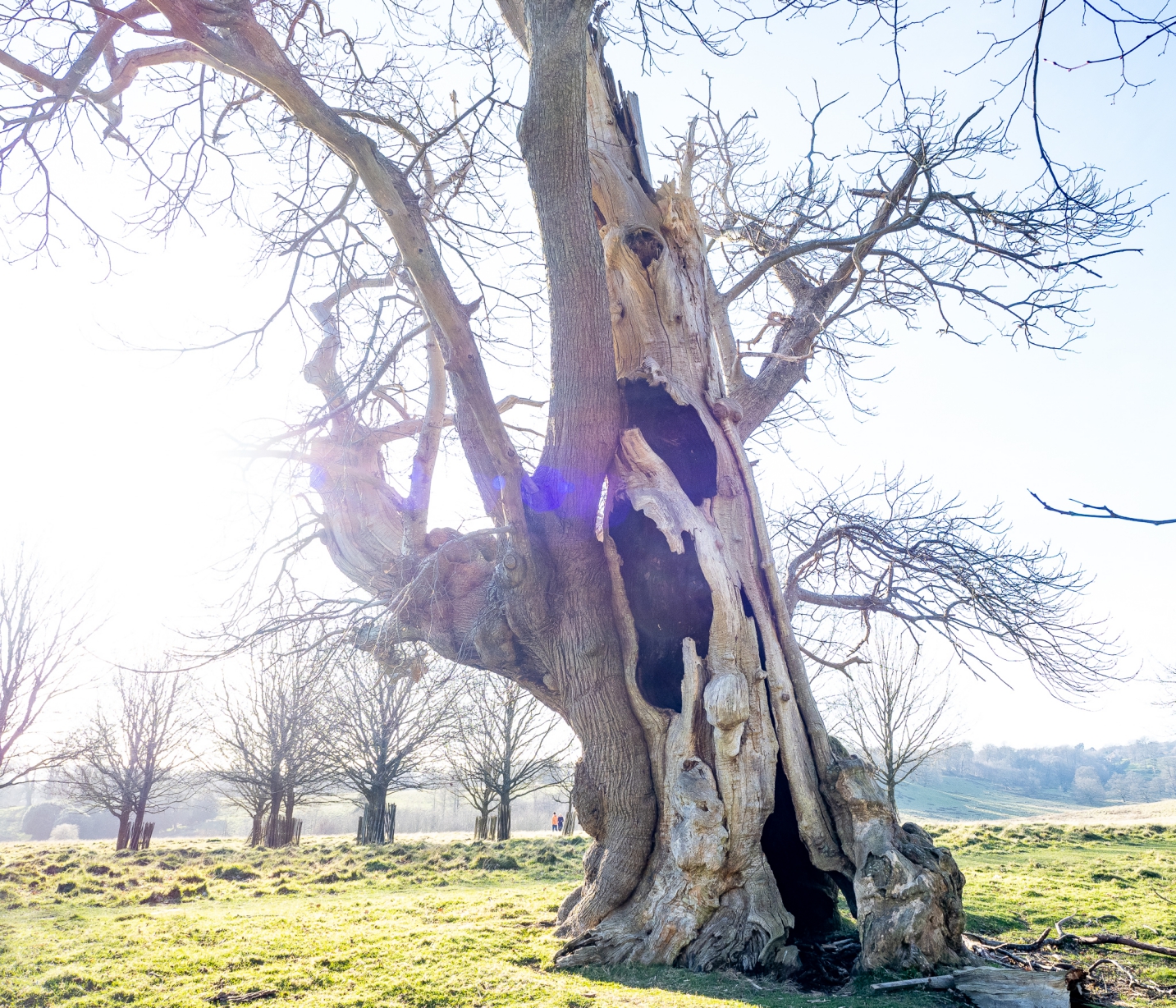
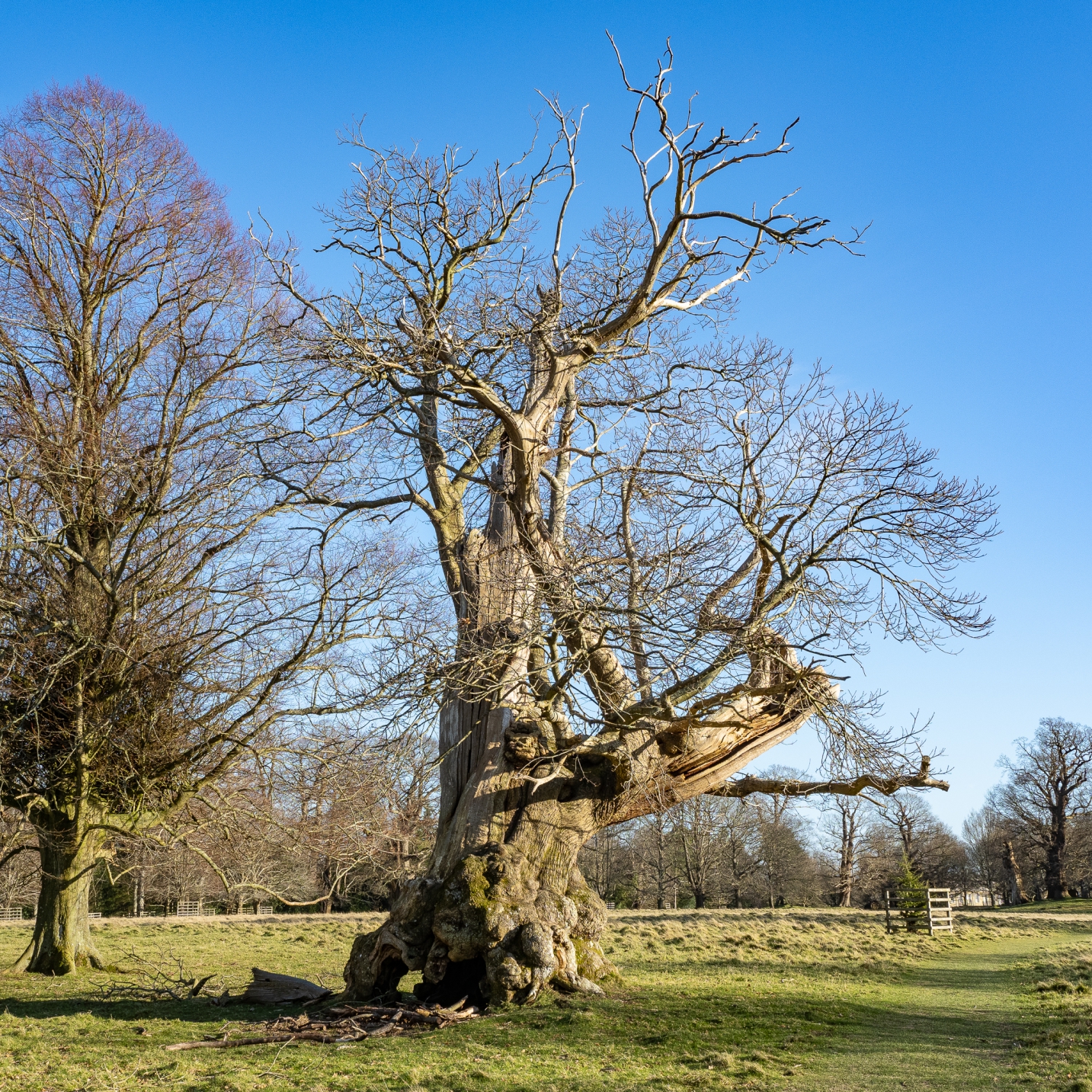
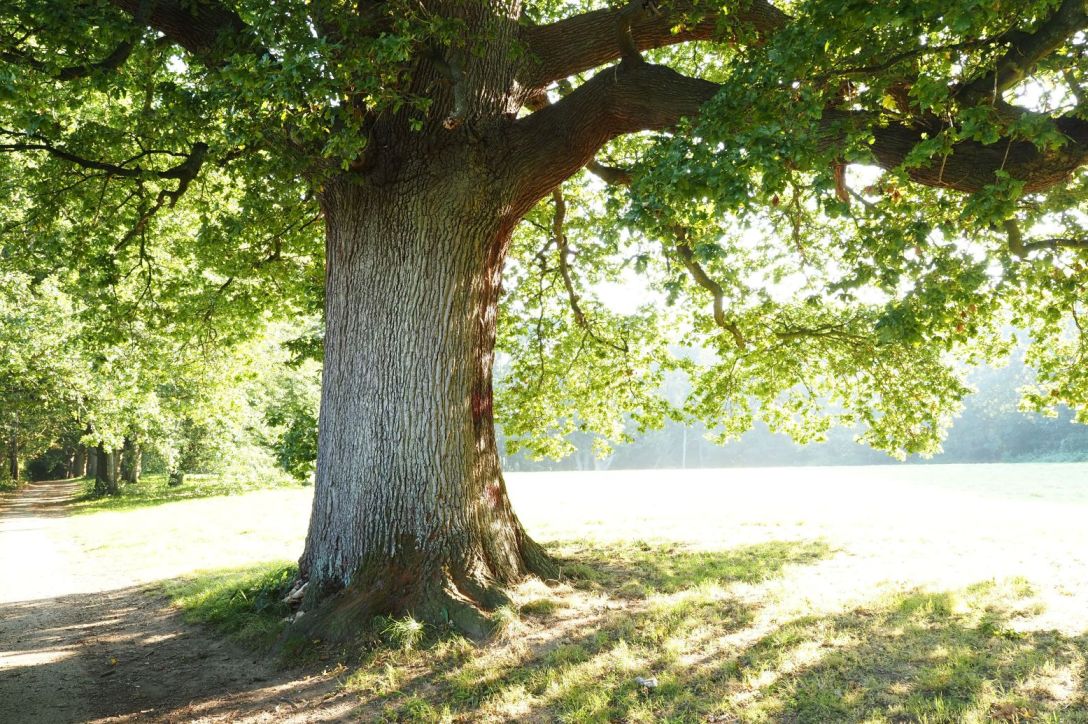
Ashdown Forest in the Sussex Weald, East Sussex, June 2024
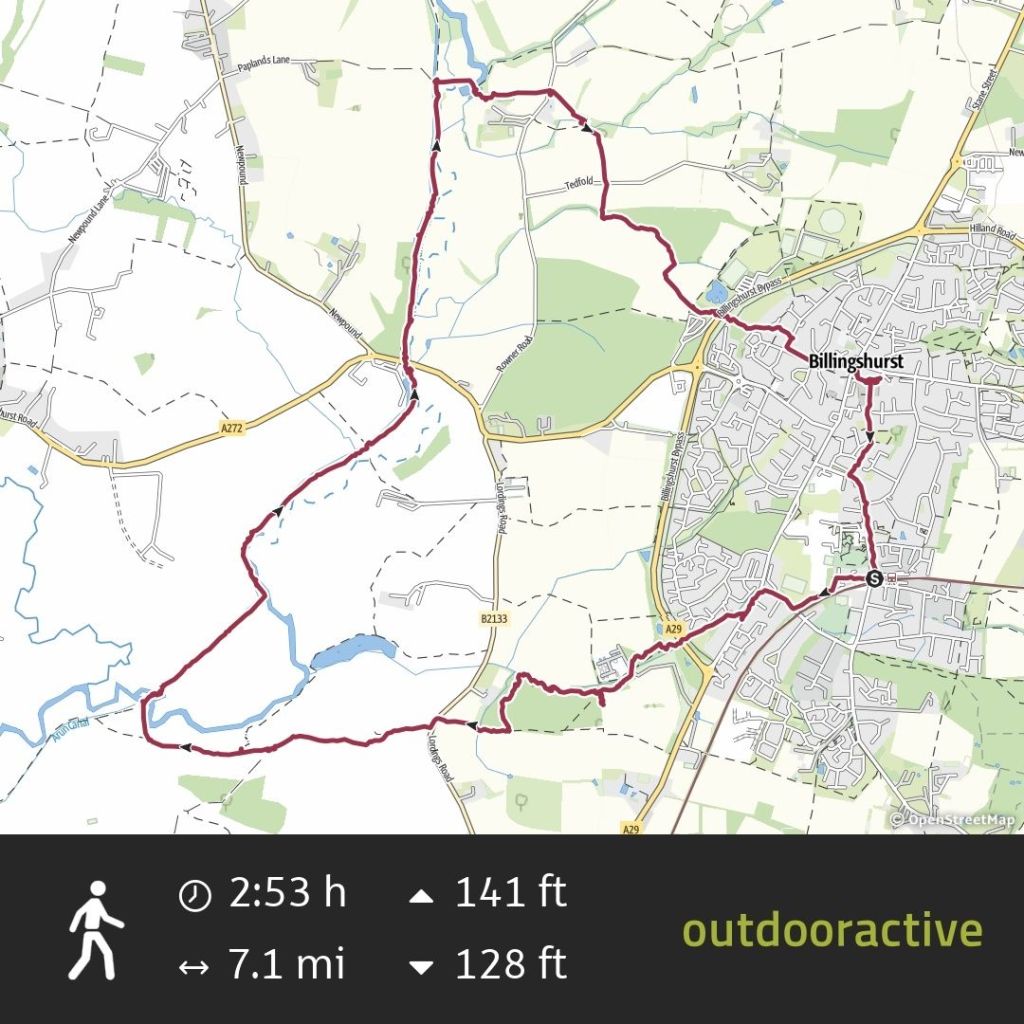
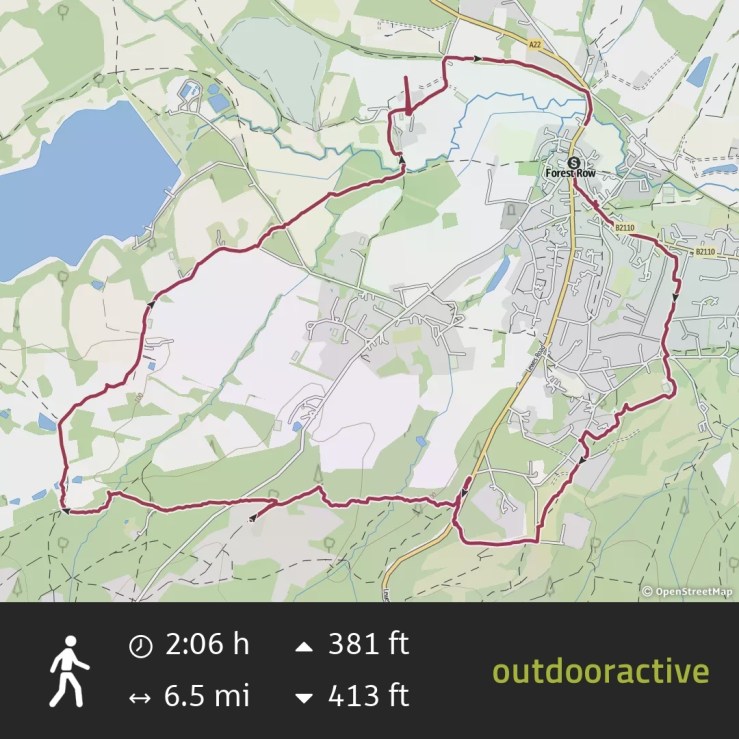
It’s time to unearth another Sussex gem from 2024 with a walk to the mysterious Brambletye Ruins. It was an after-work jaunt, starting in the village of Forest Row in East Sussex.
We didn’t stop, clocking up 6.5 miles in 2 hours which is unusually fast for me. There are a couple of B-roads to engage with so take care on those as people can be quite careless with their speed on rural roads. There are no streetlights so you may want to bring a hi-vis and a torch to make yourself visible in lower light.
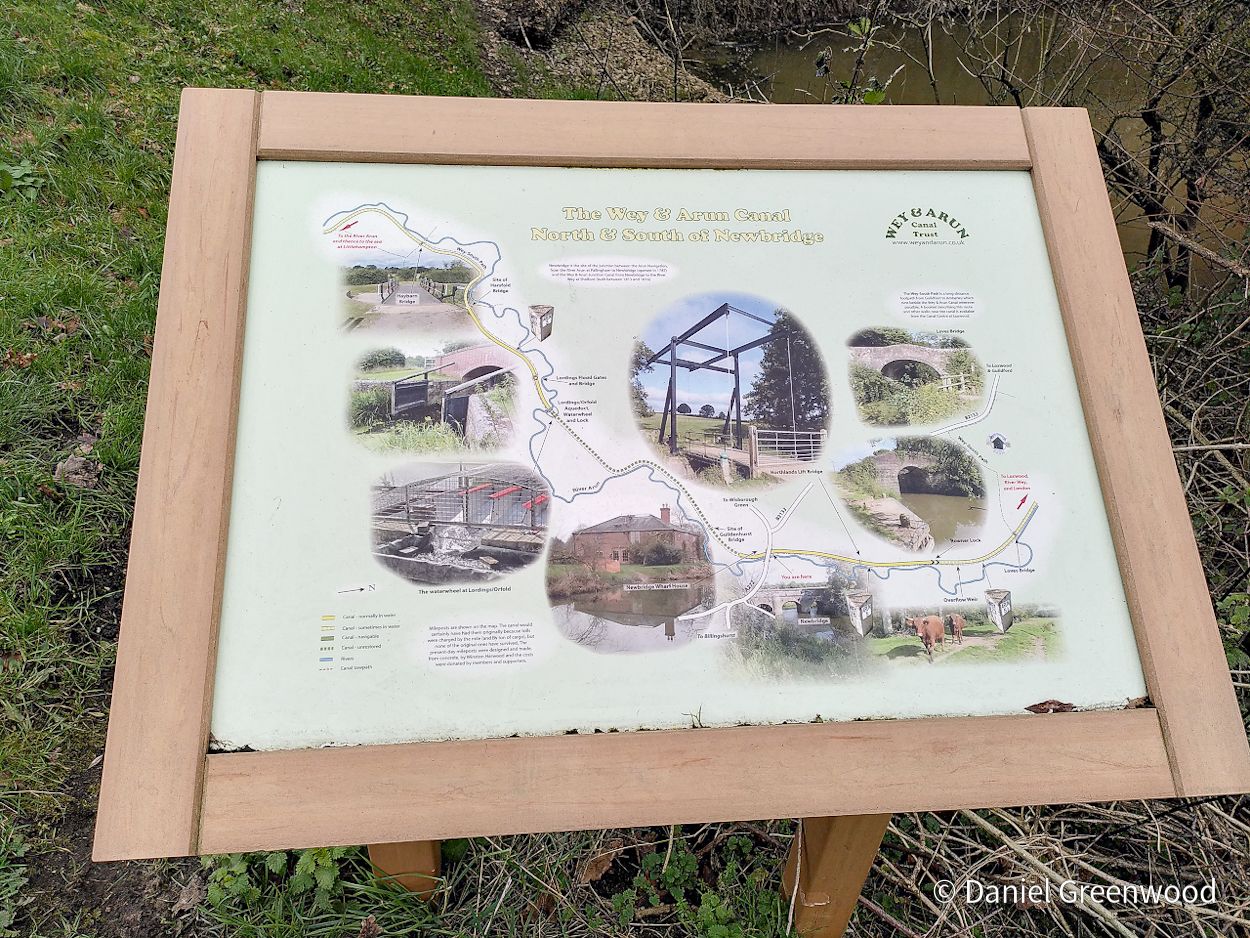
East Sussex County Council is promoting a shorter version of our walk (3 miles compared with out 6.5) along the Forest Way which you can view here. The Forest Way is the route of the old railway line that used to run between East Grinstead and Forest Row. This line was closed by the infamous Dr. Beeching, and there’s some interesting information about that:
The Forest Row railway station opened in 1866. Although a busy commuter line, it was axed with the Beeching cuts in 1966. Ironically, Dr Beeching lived near Forest Row and regularly travelled up to London on the line when he was Chairman of British Rail.
https://forestrow.co/forest-way/
Kill your darlings, as the creative writing teachers say.
This blog is a comprehensive account of the history of Brambletye (which doesn’t have a Wikipedia page!) from a local. If you want to see Brambletye in this blog you’ll have to get to the end as we left the highlight to the final stretch of the walk.

BBC Sussex recently published an article about Brambletye and a Secret Sussex podcast episode. This is an interview with Garen Ewing, a local illustrator who seems to be ‘the Brambletye Guy’. His website has a trove of information about the history of the house with a lot of interesting old images, which I wish were larger. The whole reason we did this walk was after a suggestion from my friend Edwin, who had learned about Brambletye from Garen’s crowdfunder for The Brambletye Box:

You can read more about Garen’s fundraiser on his Patreon page.
The photos in my post are a blend of mirrorless camera and phone, with the odd illustration and historical photograph where I could find some.
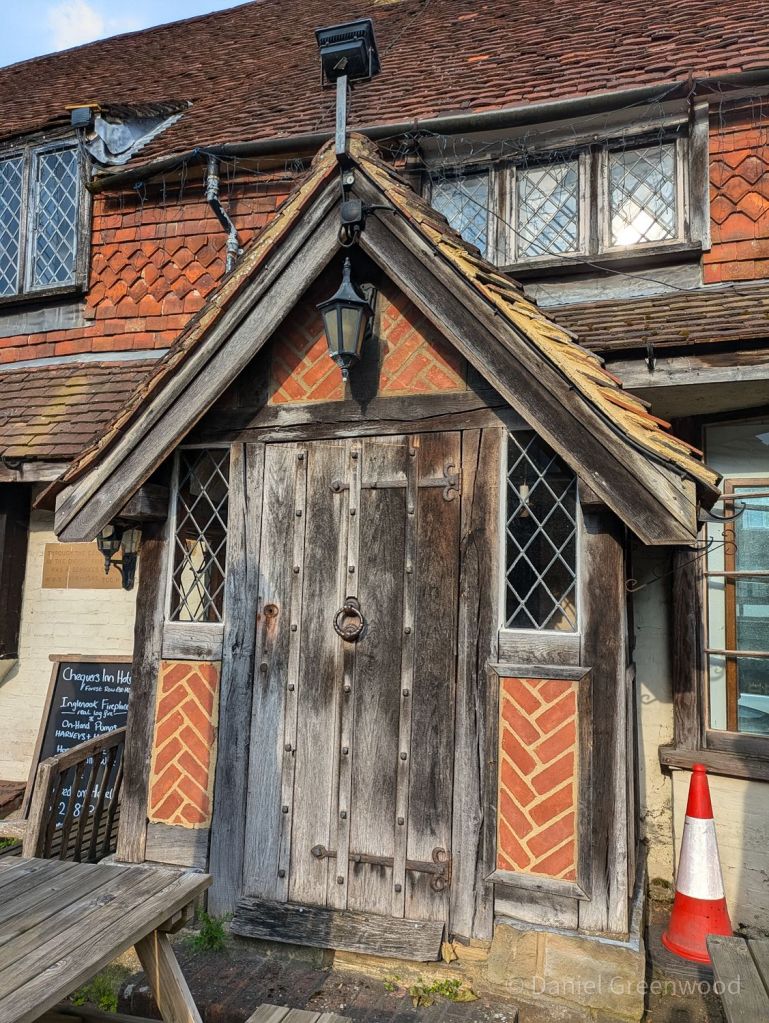

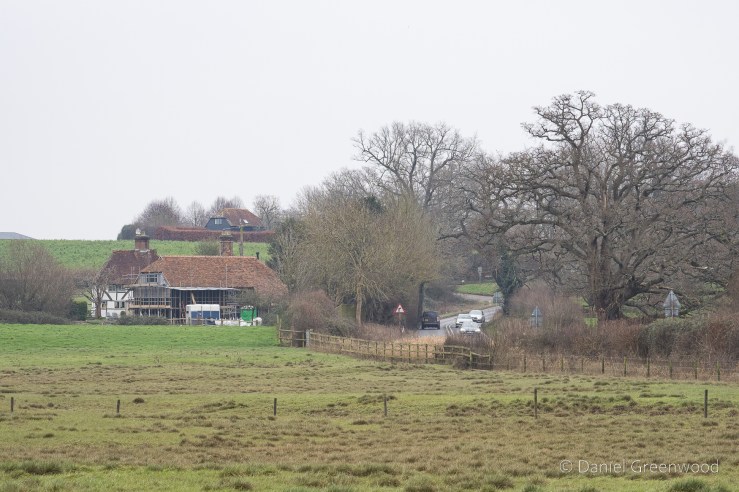
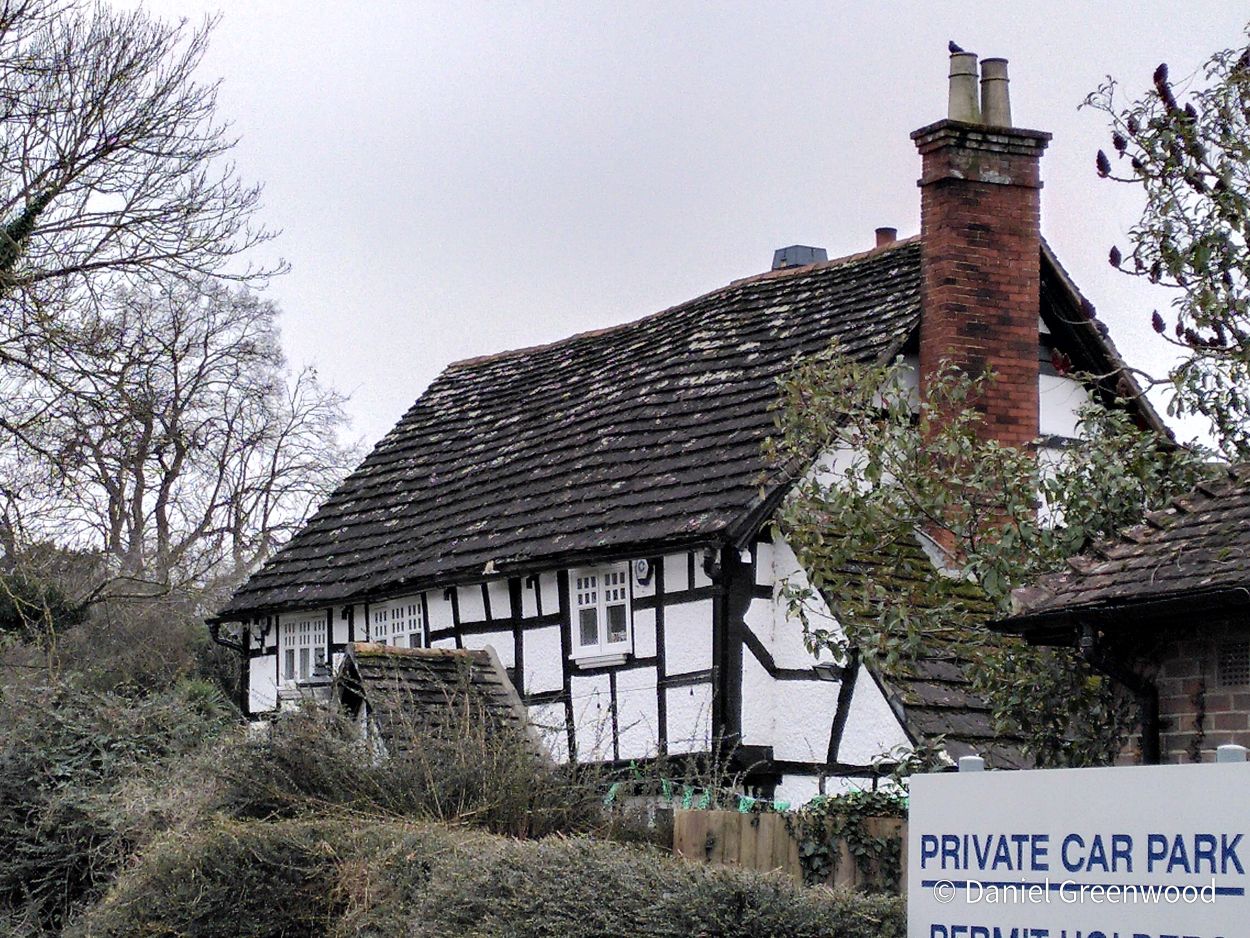
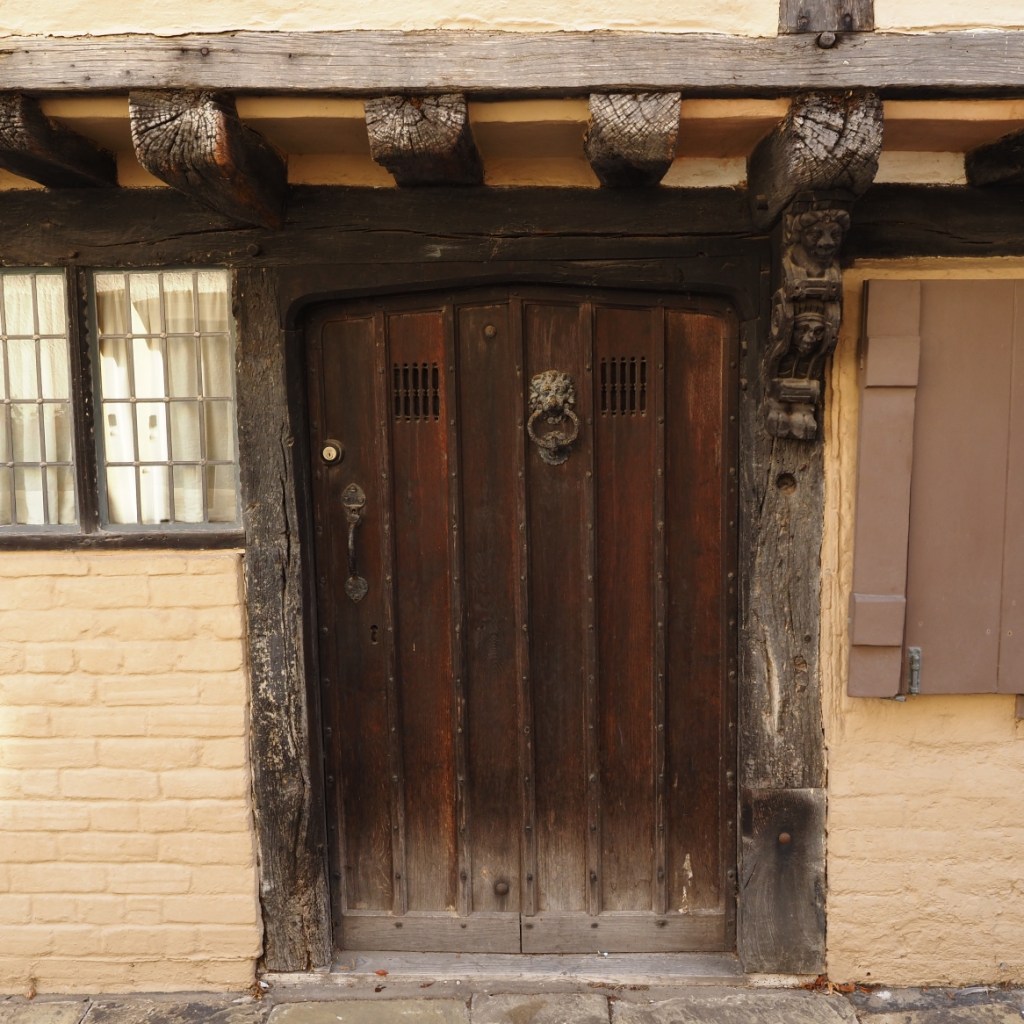
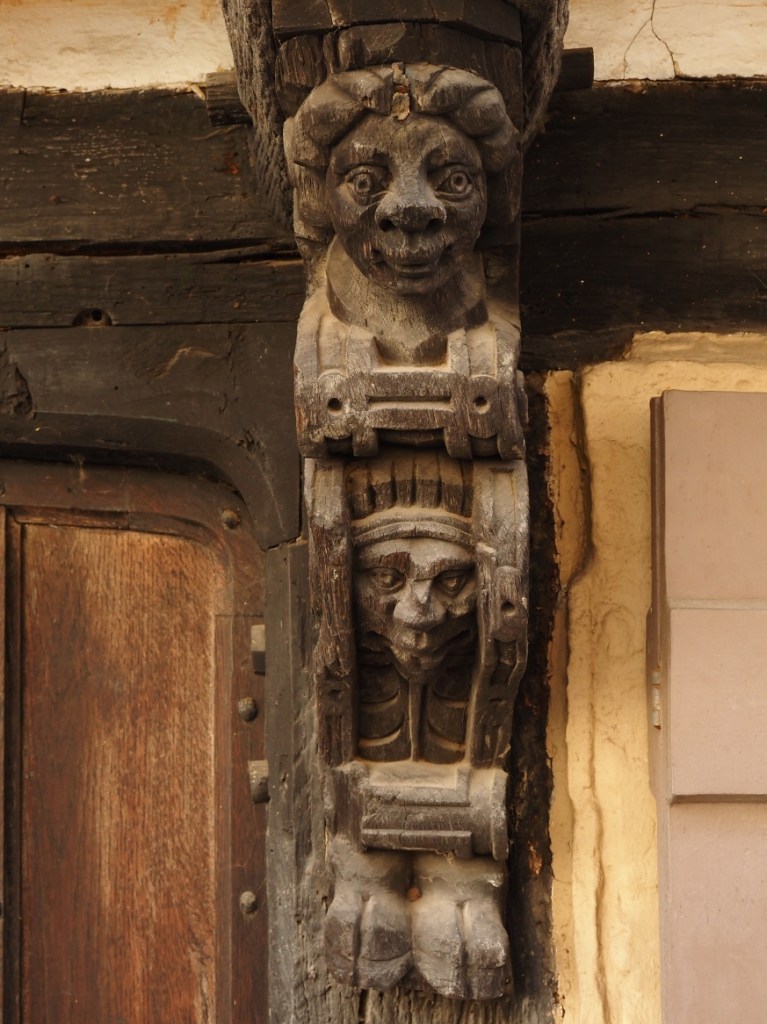
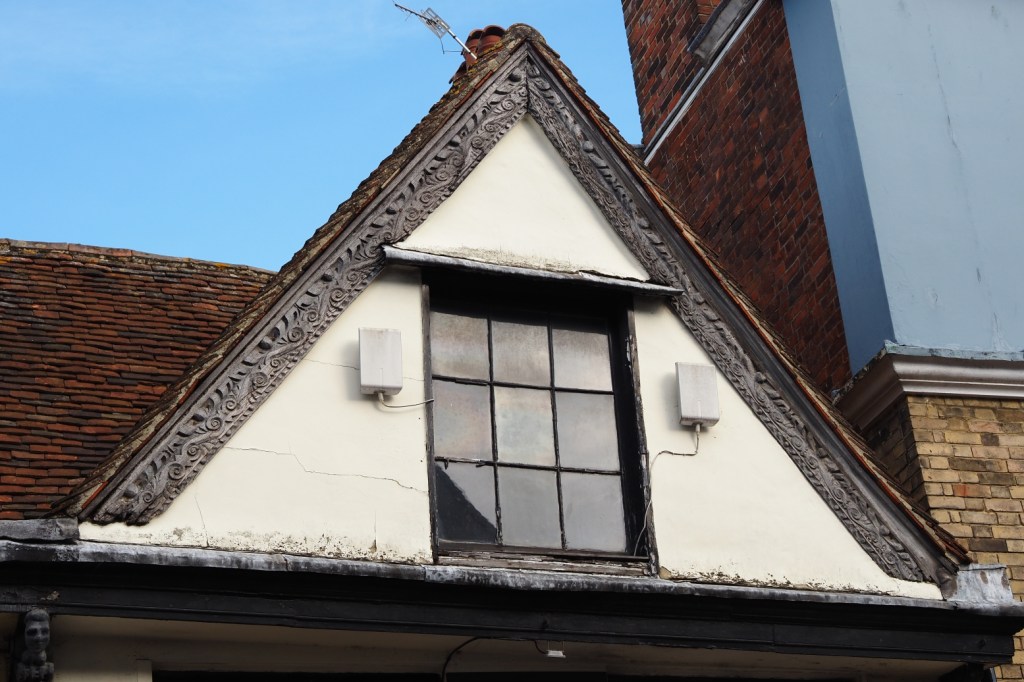
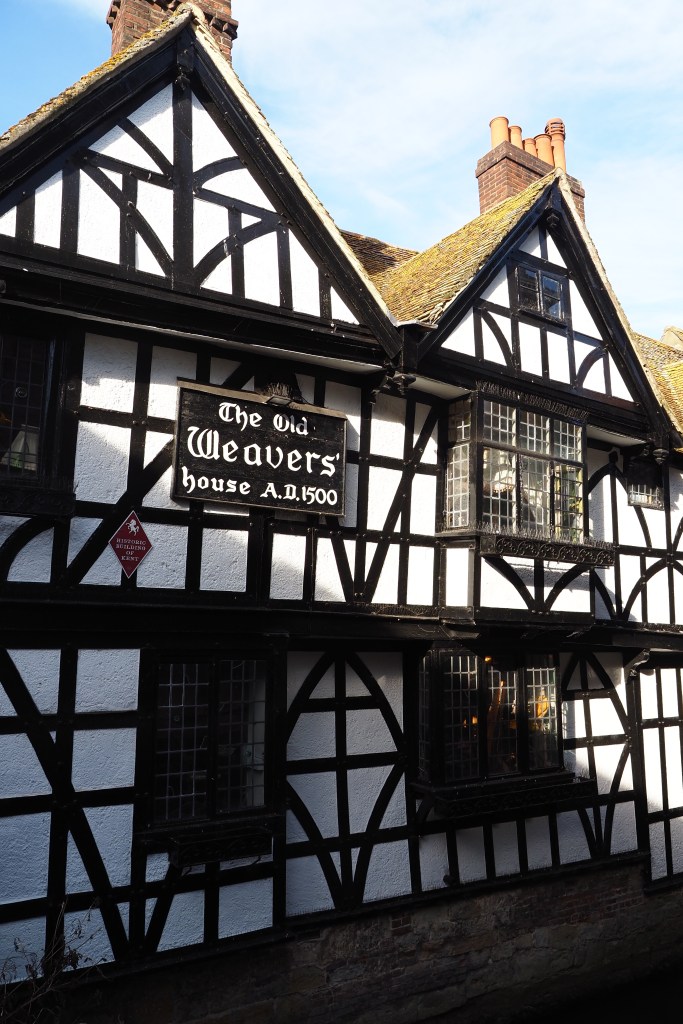
I parked in Forest Row in the village centre, where there are some typically oaky timber construction to be admired. This is an old entrance to the Chequers Inn Hotel. This is not the only reference to oak doors in this post.

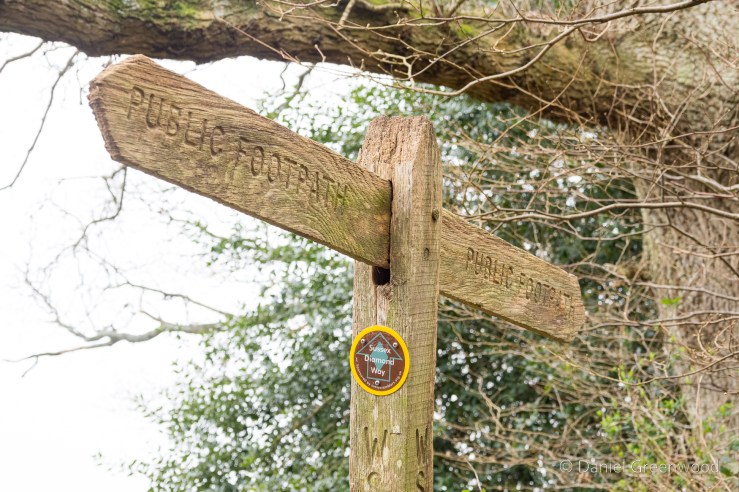
The walk leaves Forest Row by crossing a golf course, which I still find quite weird because of the tiny white eggs flying around trying to kill you. Follow the ESCC footpath signs through here.
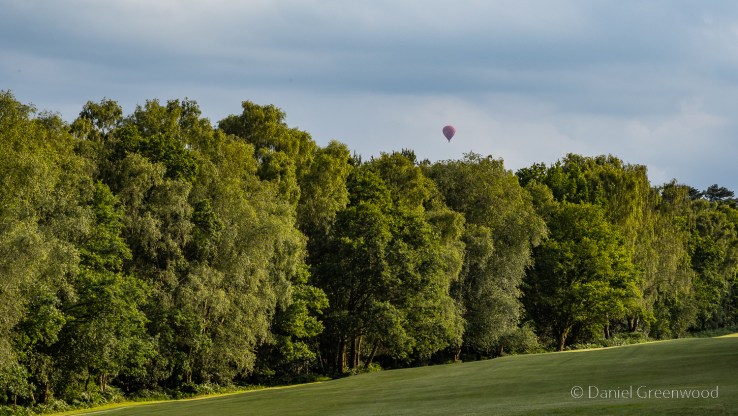

The view across the greens into the Weald was splendid. It was such a still evening, we could see a hot-air balloon beyond the birch trees in the distance.
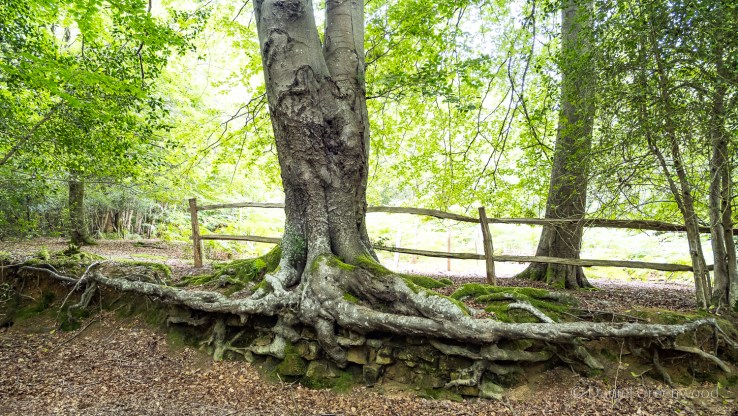

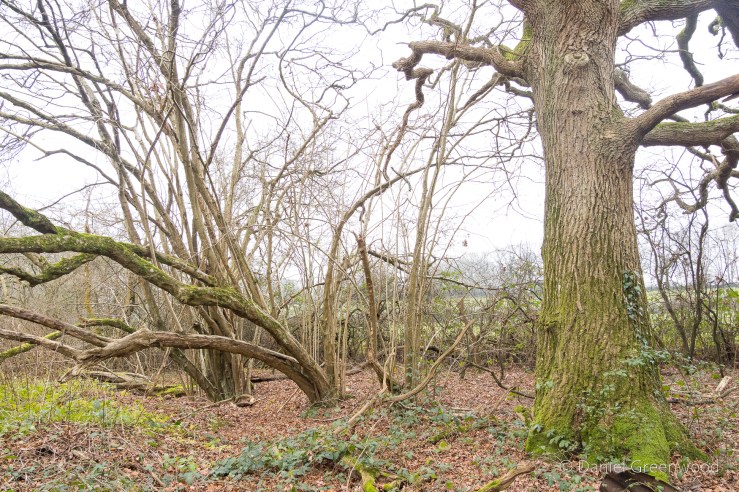
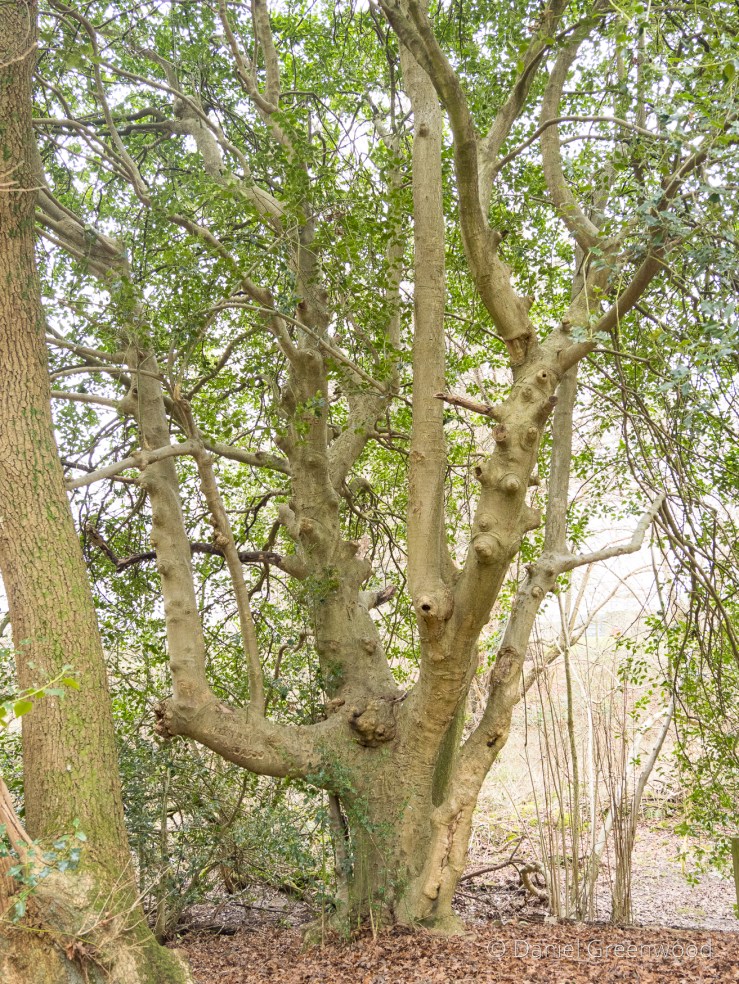
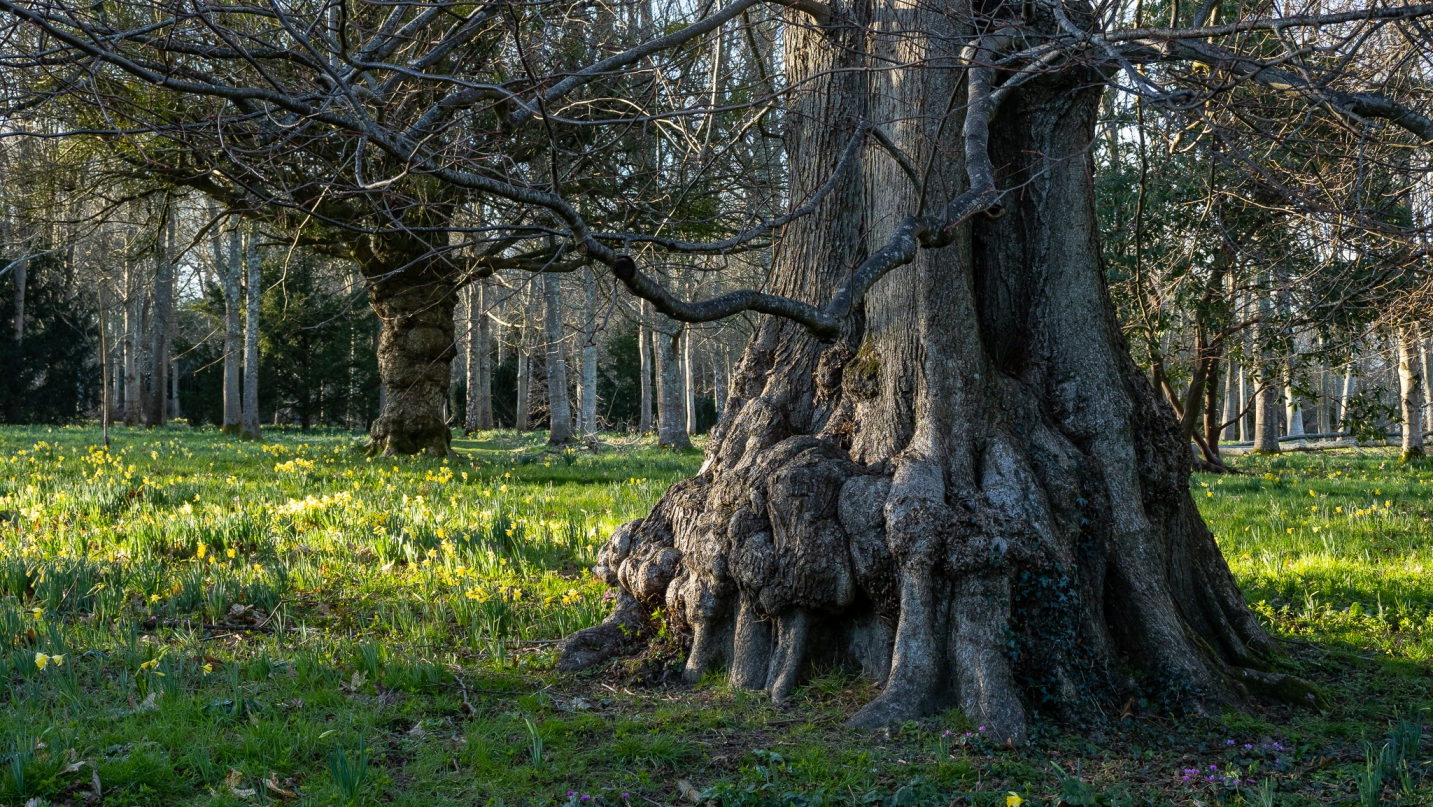
Surviving the golf course, you enter into the heathy woodlands so typical of the Ashdown Forest area. This is something you can see along old footways, a mature beech tree with its roots exposed. It’s a nice indicator of how close to the surface tree roots can be. The root has adapted to life above ground and become more like a branch. It looks like there are some bricks or stones under the roots, so perhaps the tree grew on top of a wall.
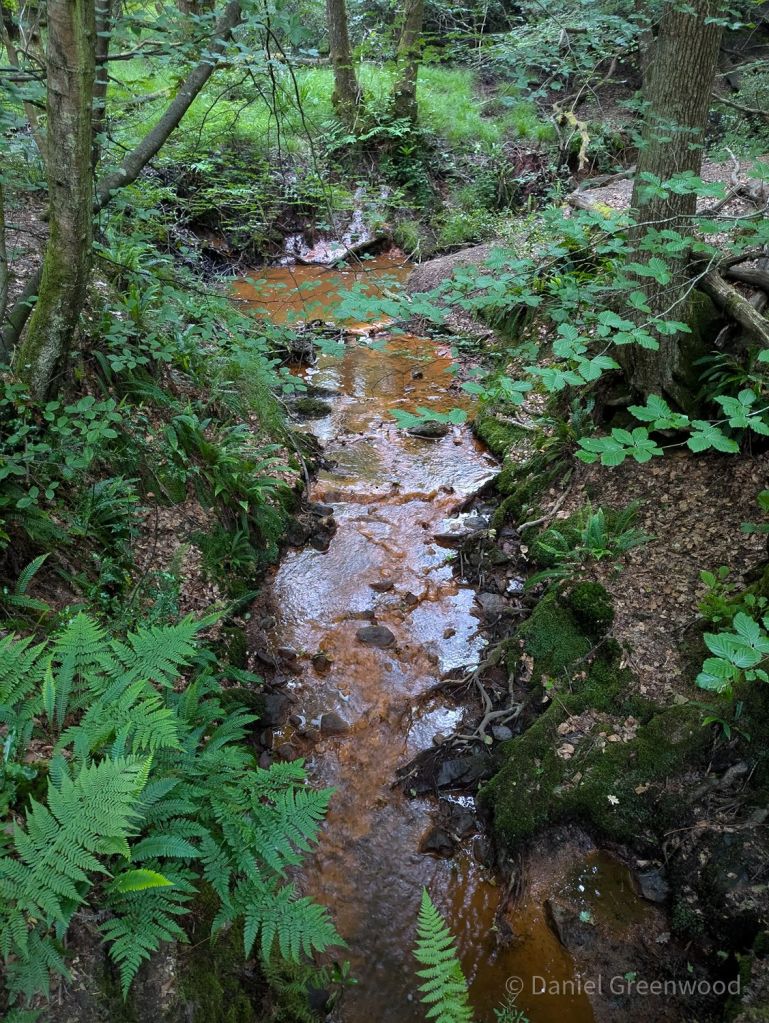

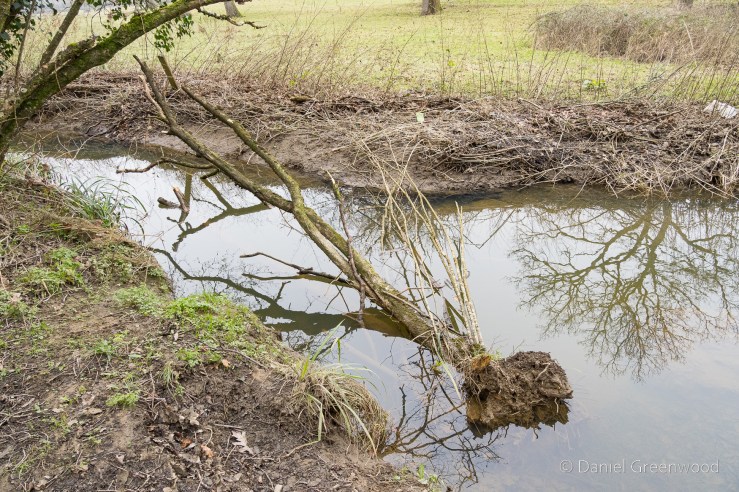
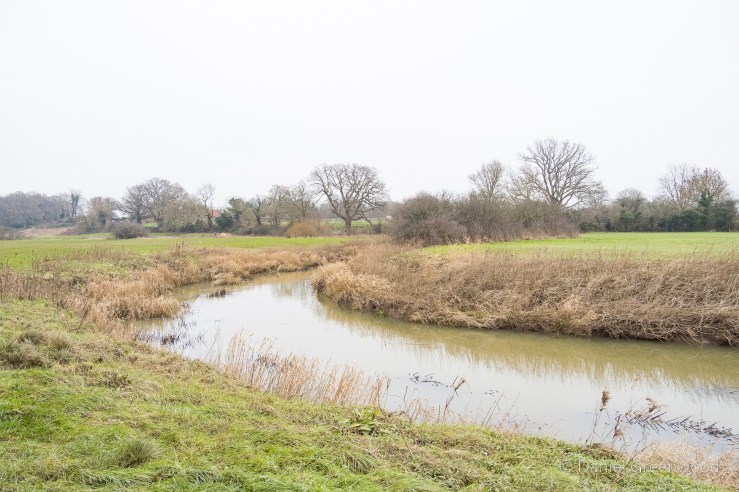
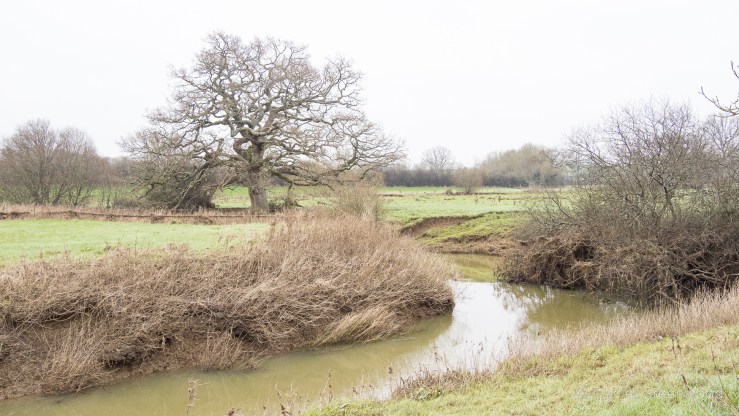
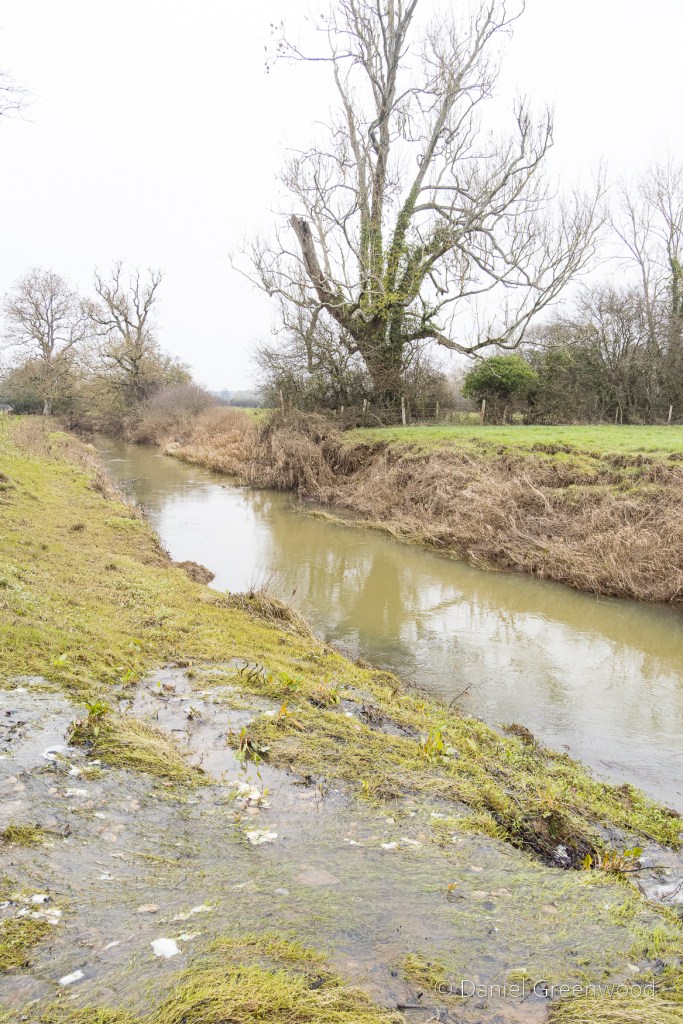
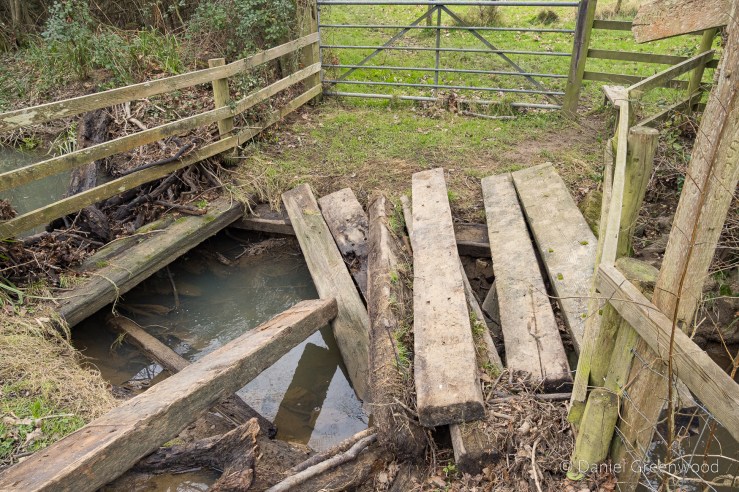
We passed one stream which is typical of those in the Ashdown Forest. This stream had the brown-orange hue of a Wealden ghyll, caused by the iron ore discolouration that made the area so attractive for the famous iron works of centuries past.
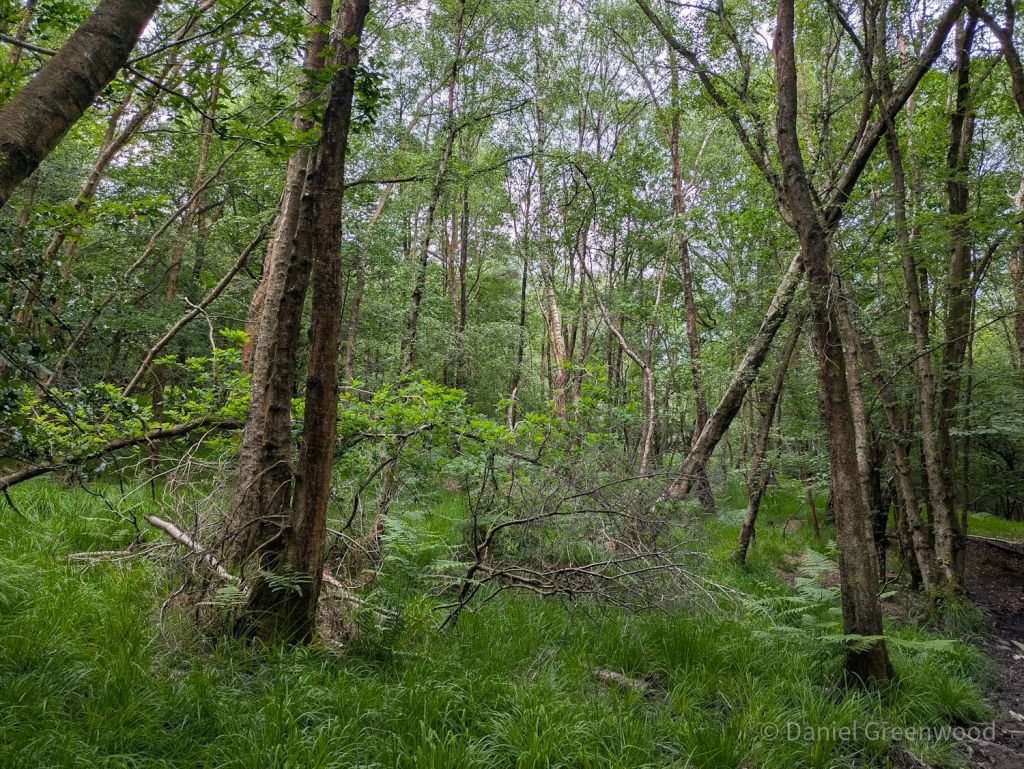

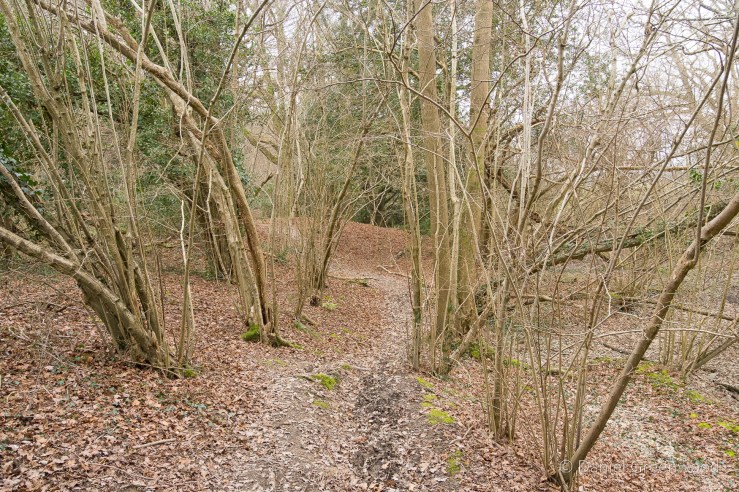
The woods were a tangle of birch and honeysuckle. I’m never sure if these are truly ancient woodlands or recently wooded heathland, but the sighting of the plant below is helpful.
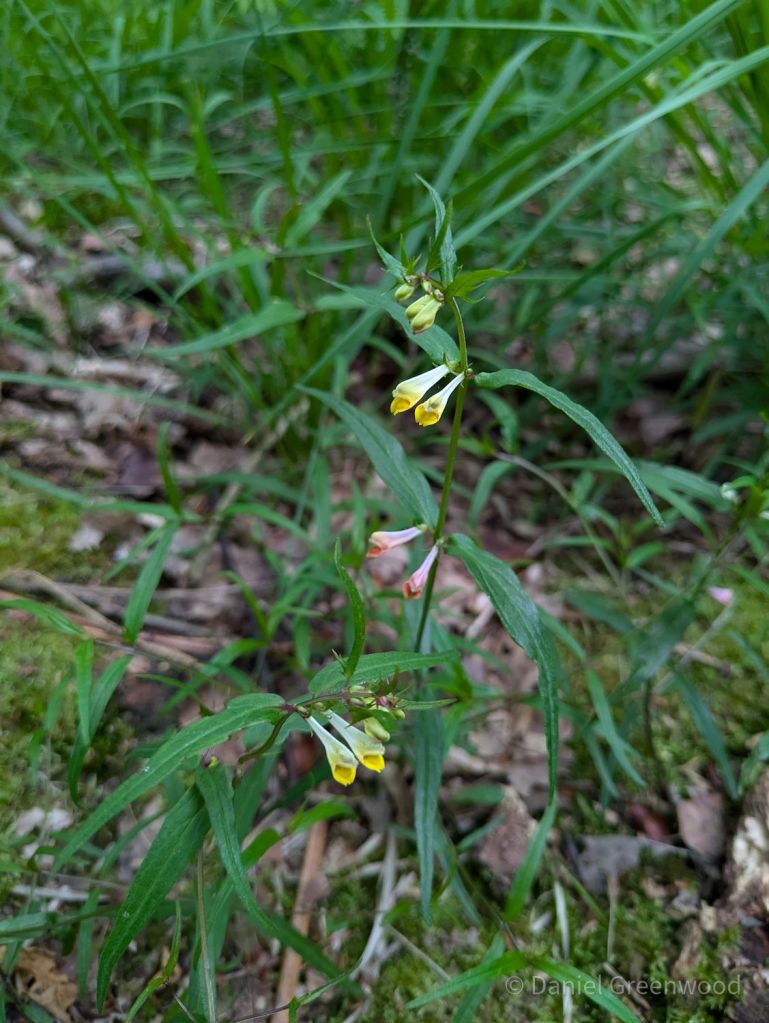

Common cow wheat is an ancient woodland indicator and is far from common. I’ve found it in ancient woodlands around the western side of the High Weald. It used to be found in south London’s oak woodlands but has been lost since the 1980s. Plant diversity declining before our very eyes. It’s in the figwort family, along with yellow rattle and foxglove, of which more later.
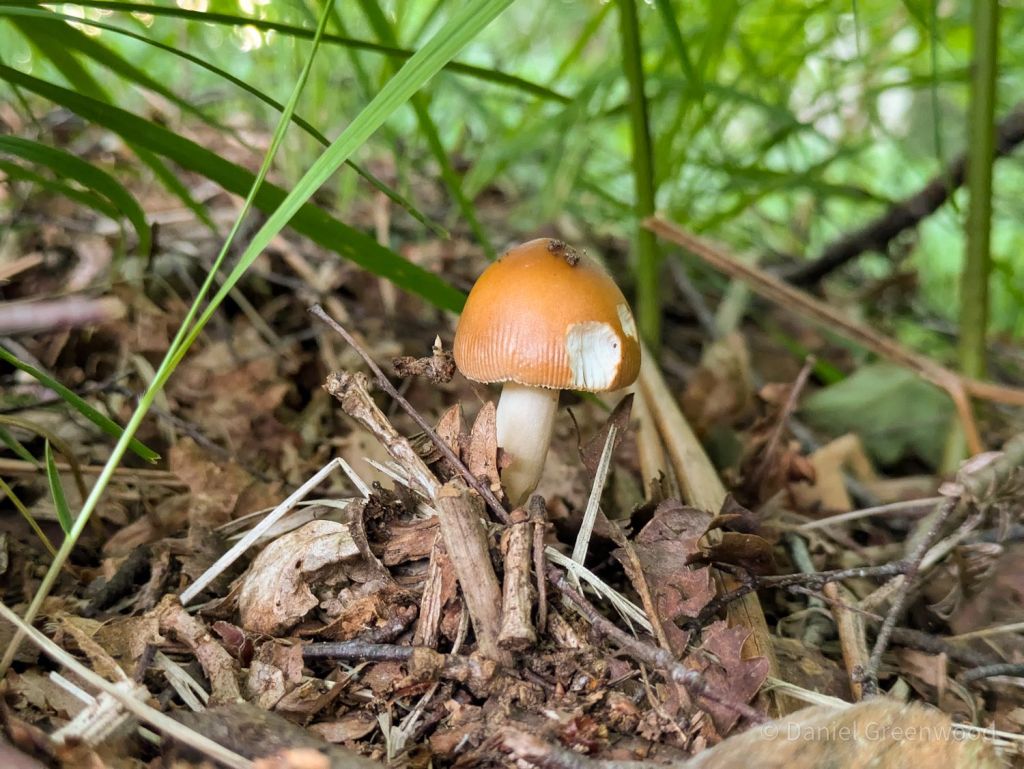

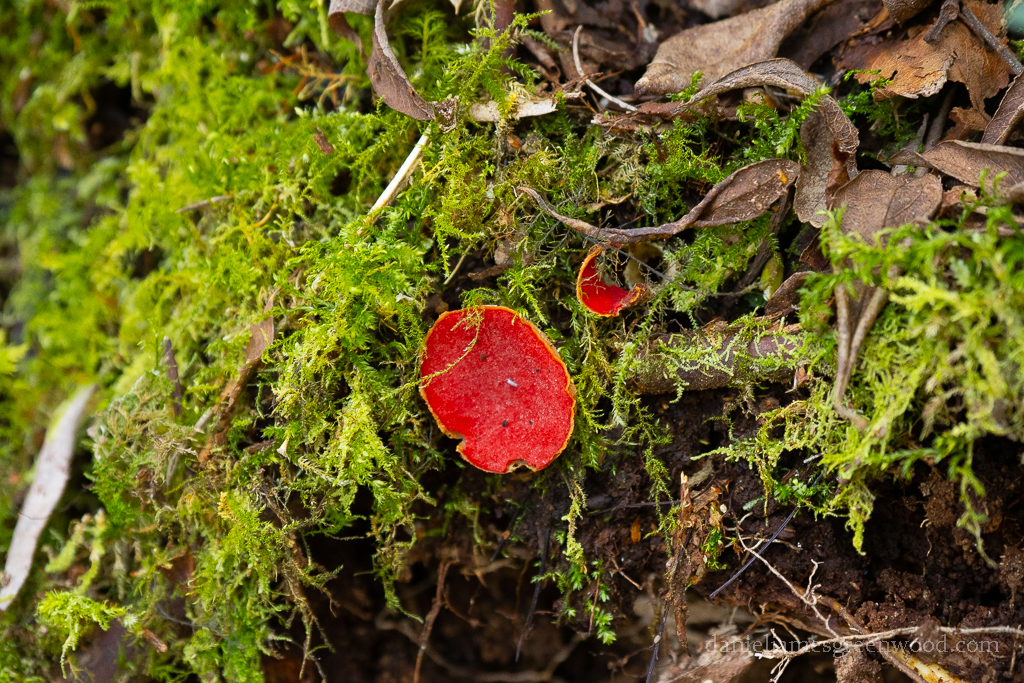
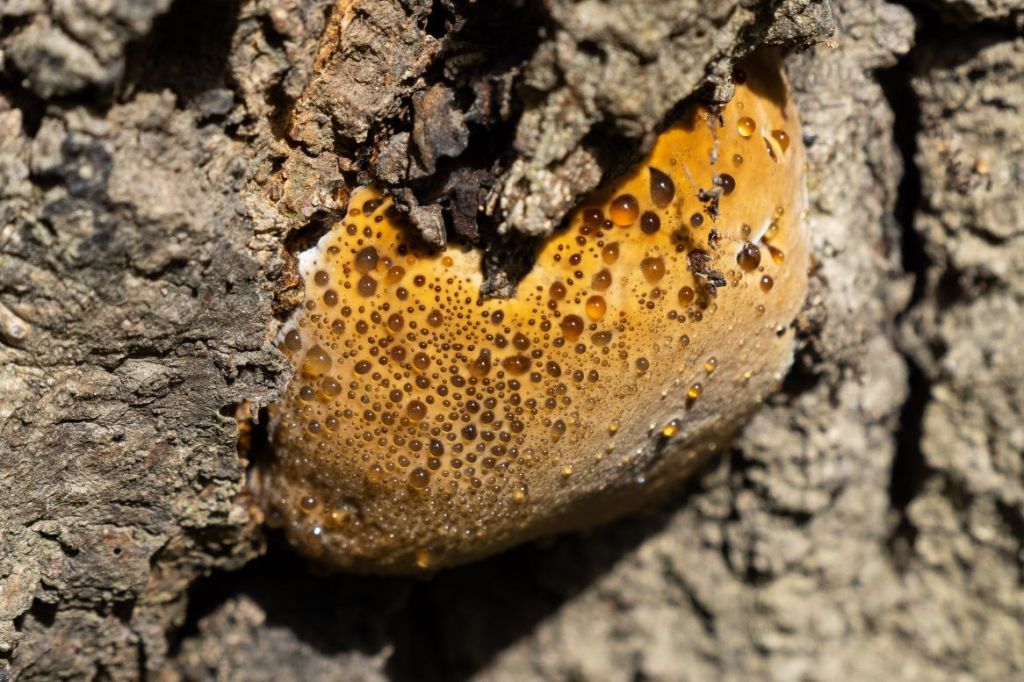
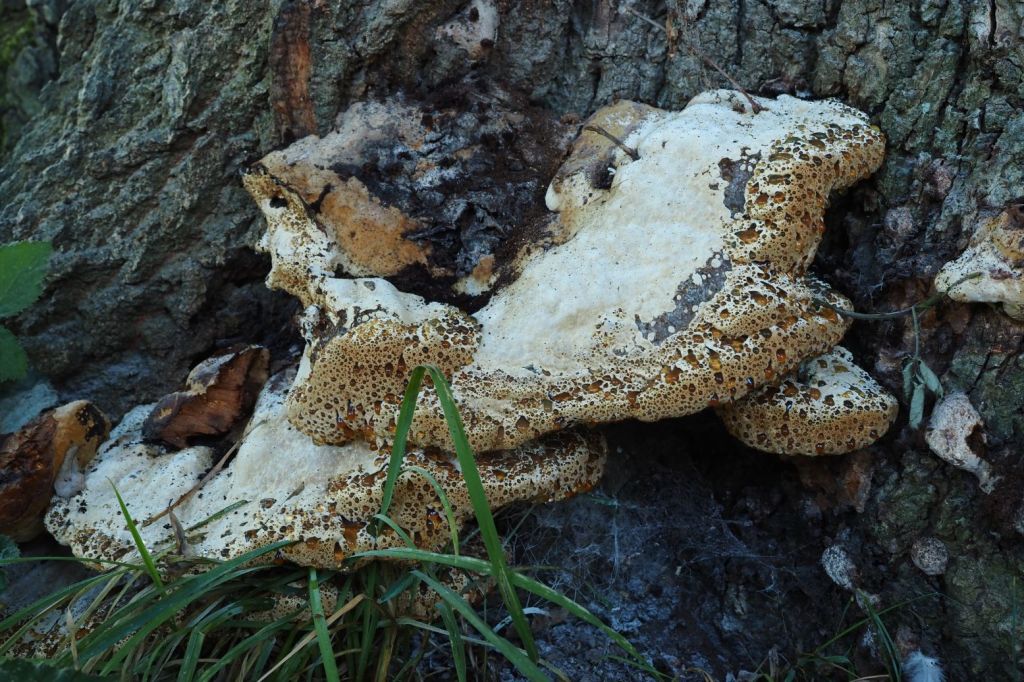
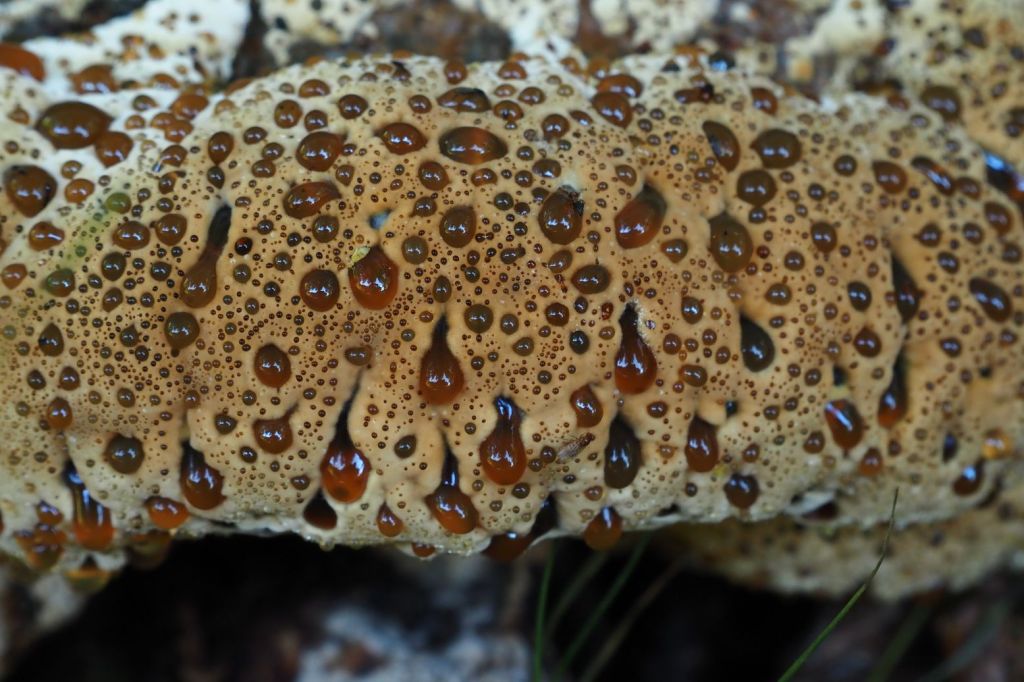
June can be a month of mushrooms, so I wasn’t hugely surprised to find this tawny grisette. For more mushrooms have a look at my Fungi Friday blog. After this we left the woodlands.
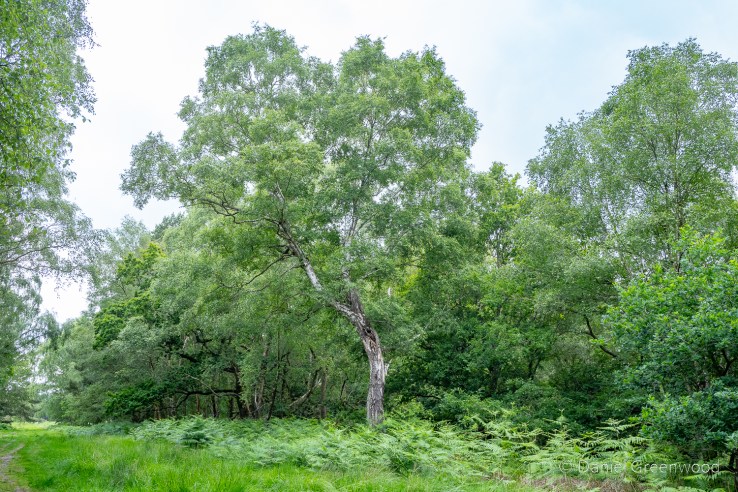

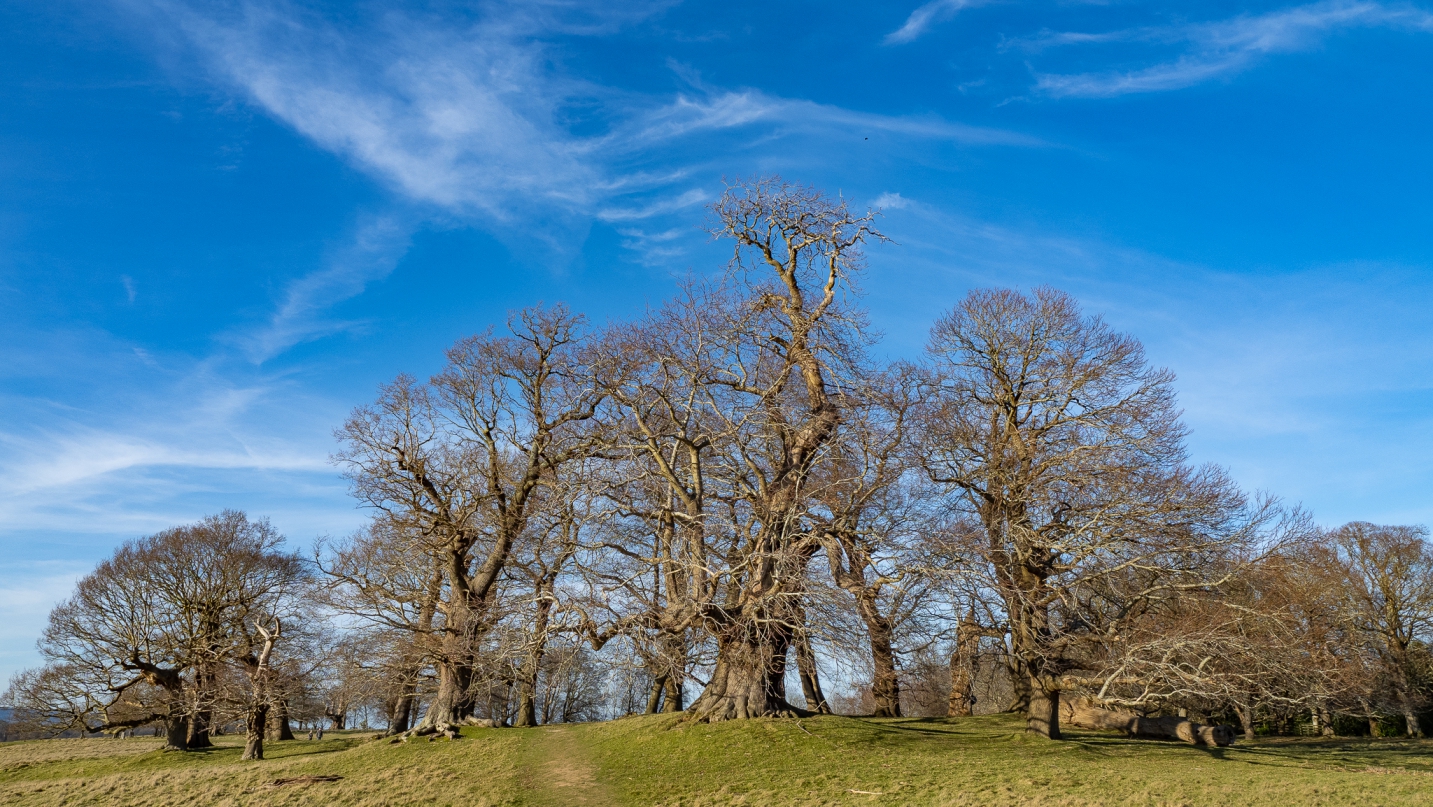
These heathlands are very birchy, brackeny, oaky and rushy, much like the New Forest.
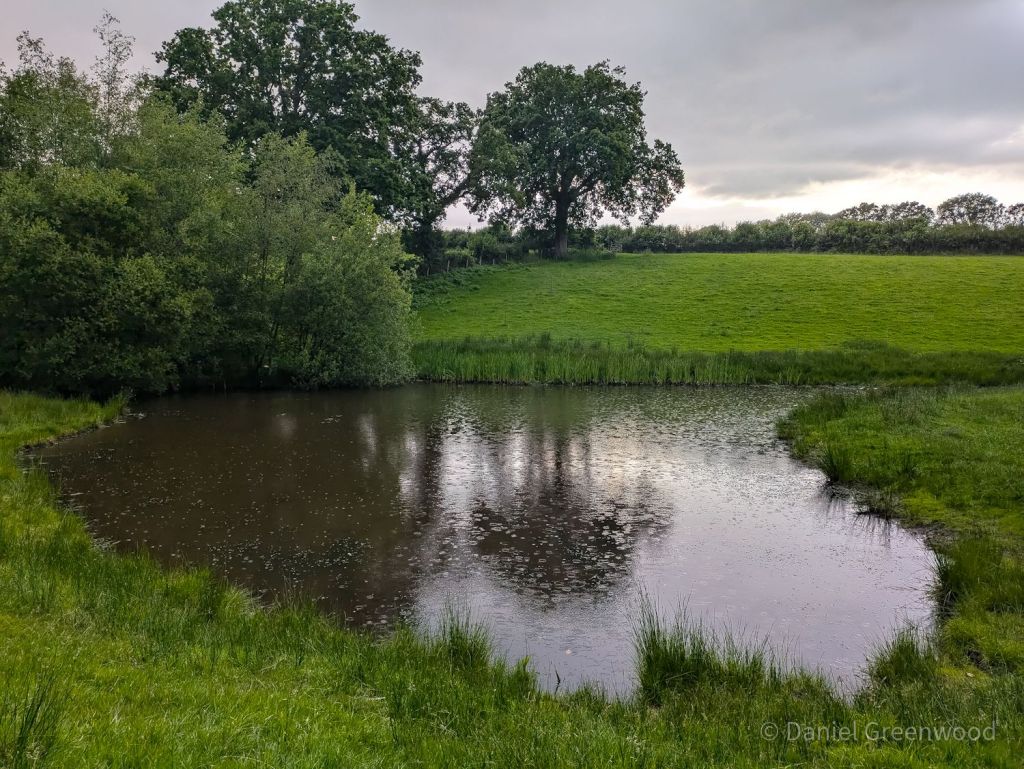

I was intrigued by this wonderful pond, one of a network of three running east-west. It’s so large and, looking at the map, is clearly part of an historically wet landscape. The placenames nearby include Alder Moors (alder is a tree of wetlands), Hollow Shaw (hollow probably a place where water pools), Mudbrooks House, and Spring Hill Farm.
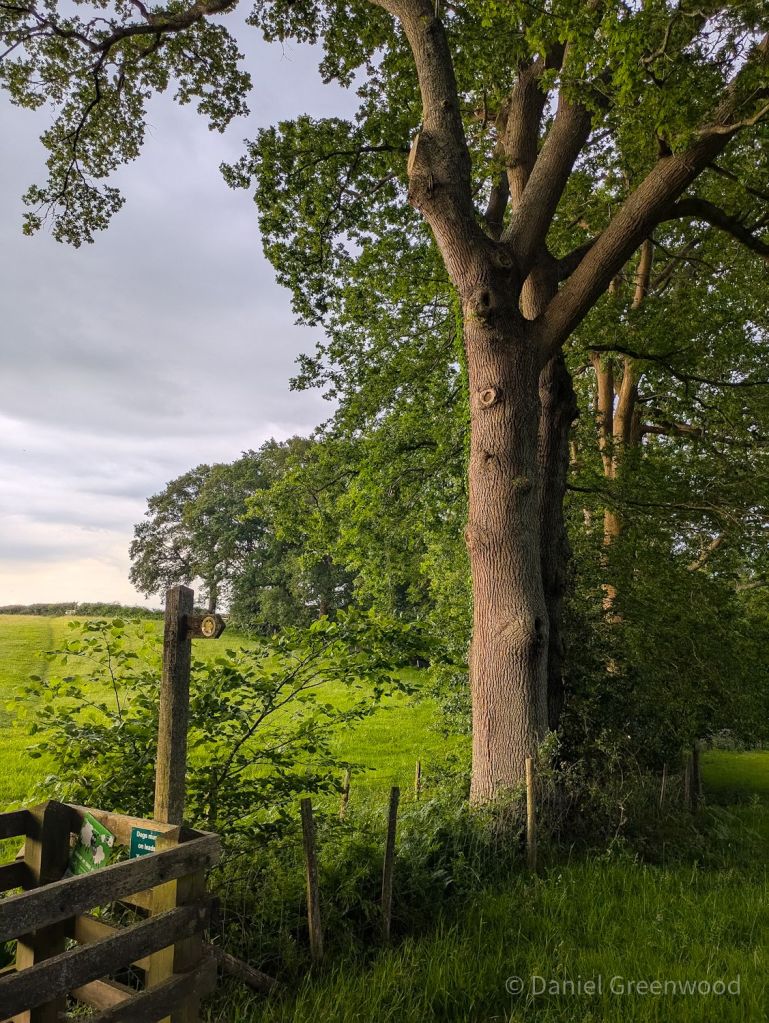

When the walk turns north out of the woods you pick up the Greenwich Meridian Trail. My parents used to take me and my sister to Greenwich Park most Sundays when we were kids, when it felt more like a south London park than a mass-tourist attraction. It’s nice to feel that connection. The Meridian Line runs through nearby East Court at East Grinstead, which this walk will take you to.
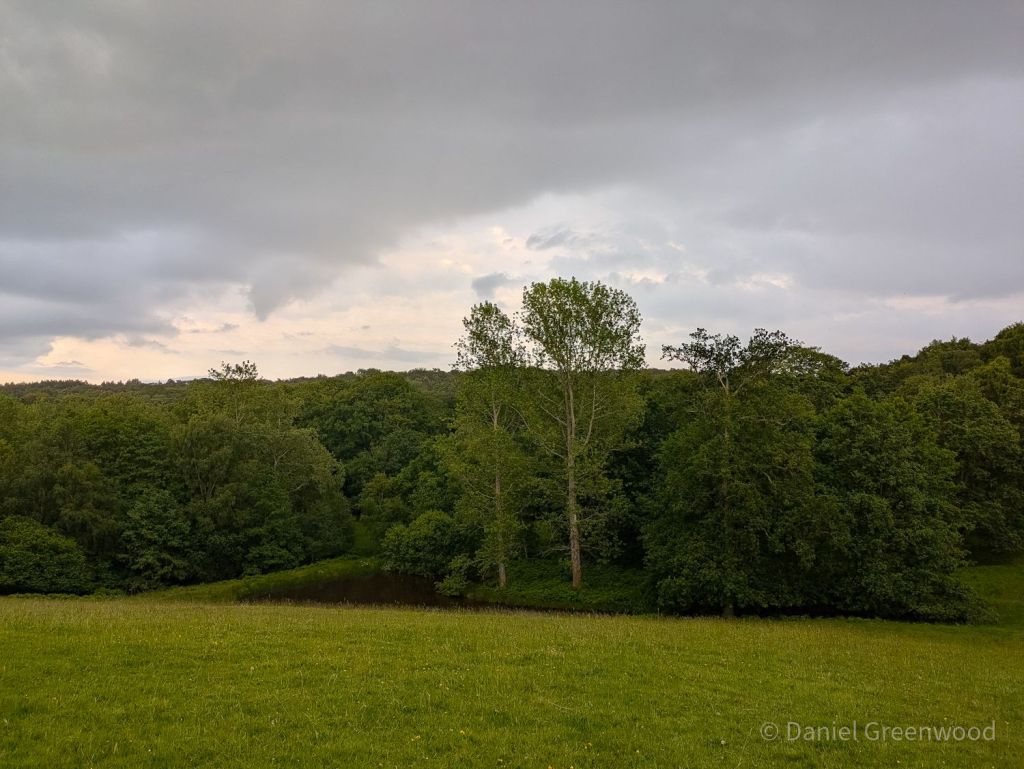

This is a phone pic looking back at the woodland we passed through, a large pond at the bottom of the slope.
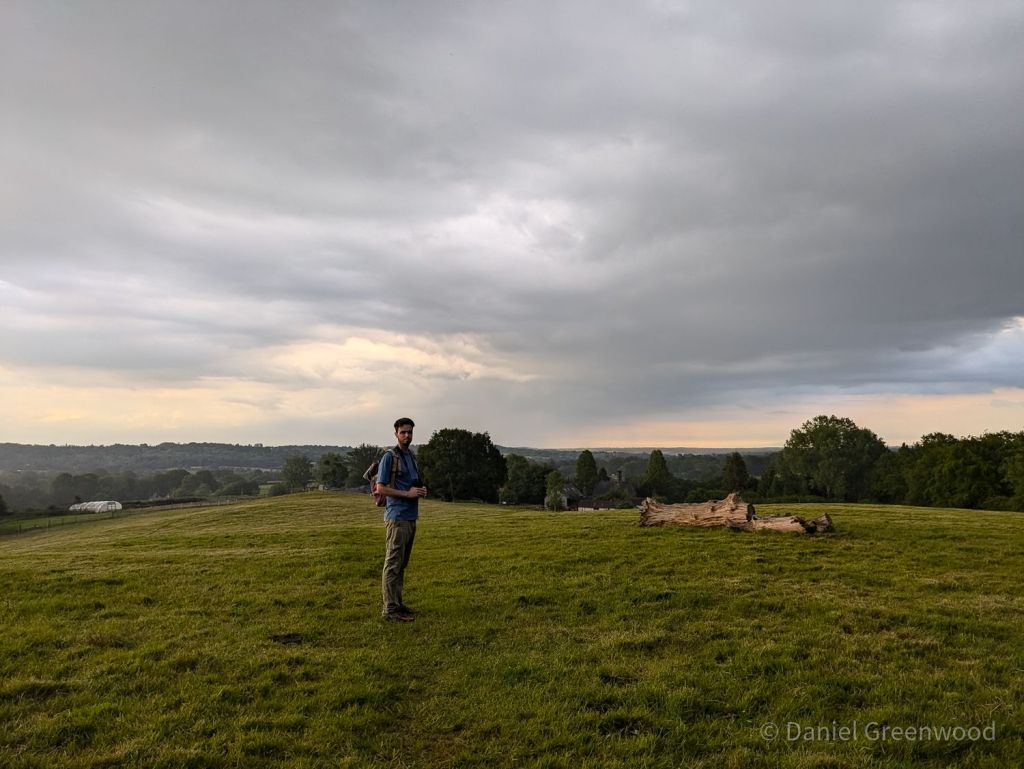

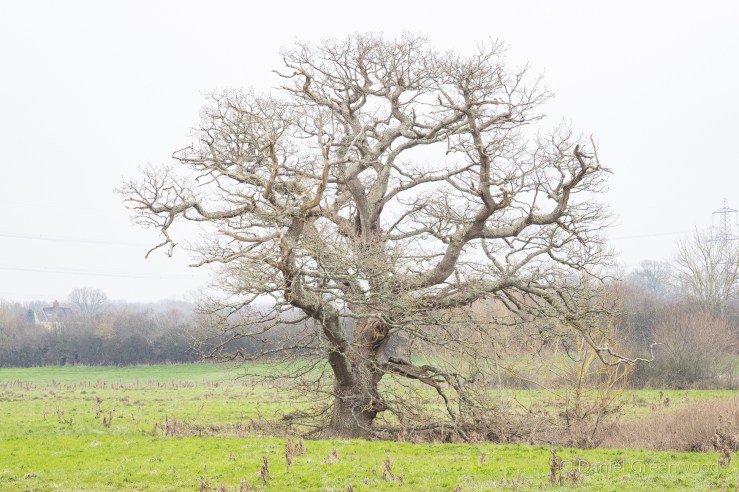
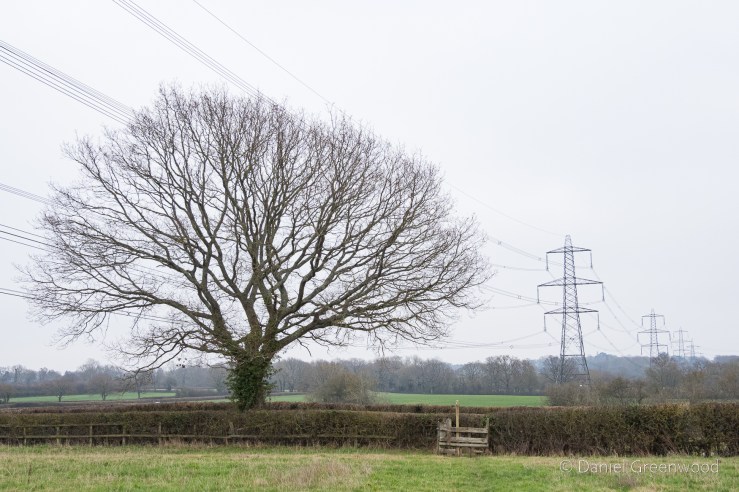
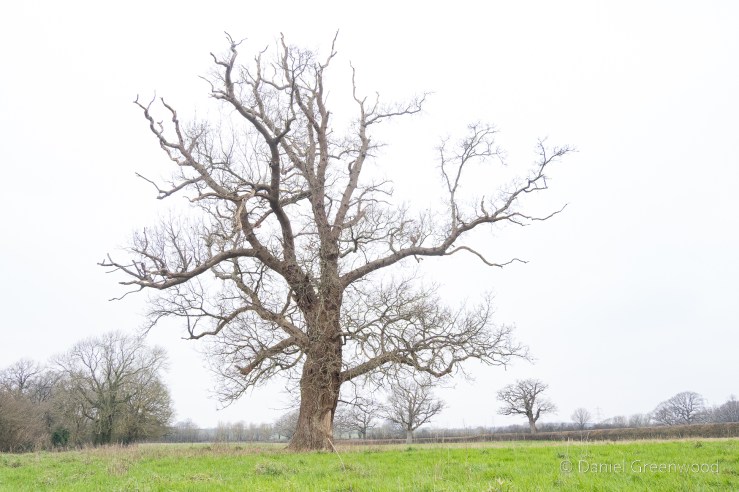
On higher ground you have view towards Mid Sussex. For some reason the trunk of a dead oak rested up there on the snooker table grassland, presumably where it fell.
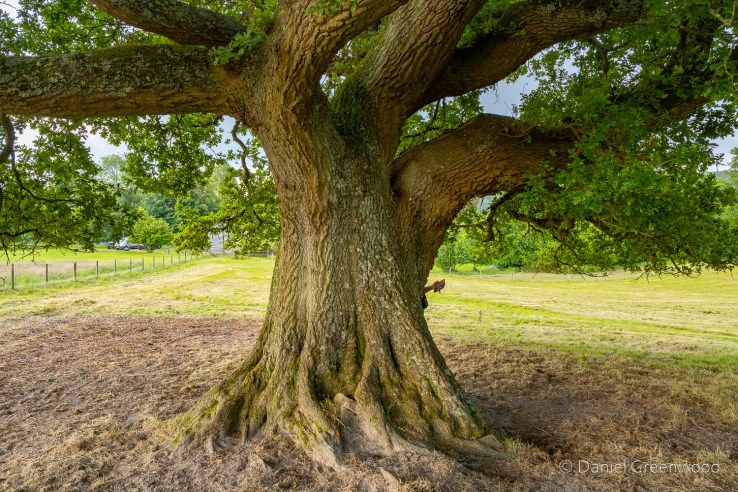

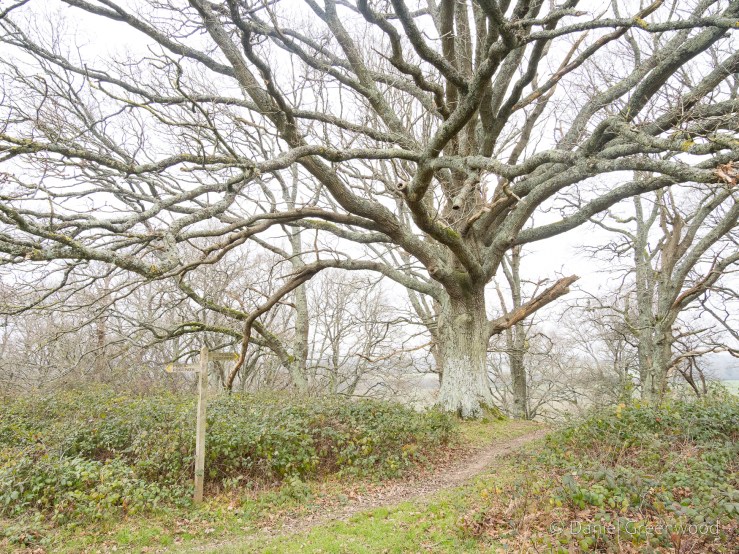
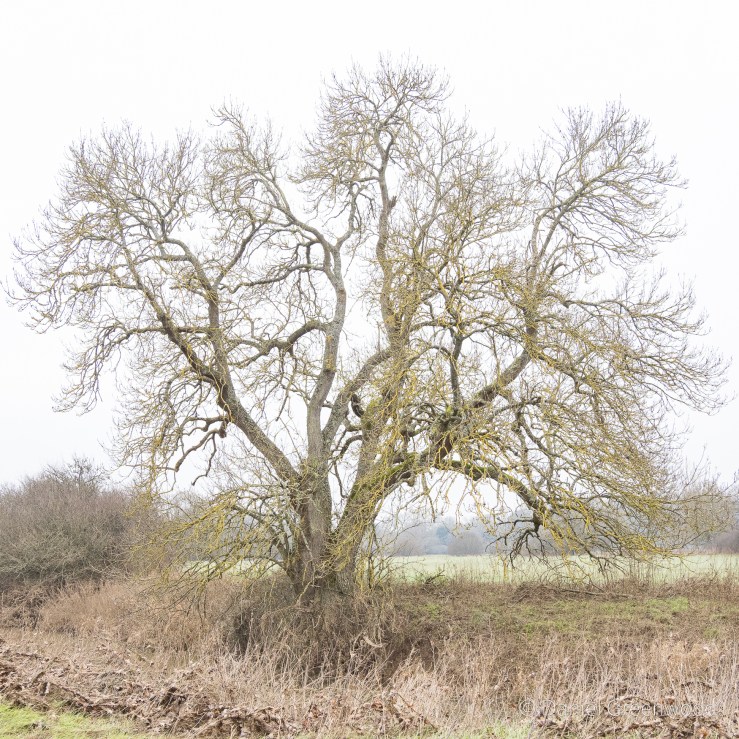
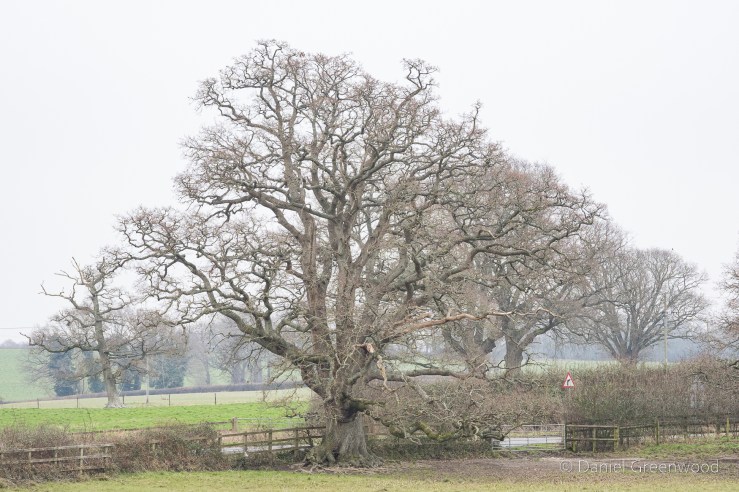
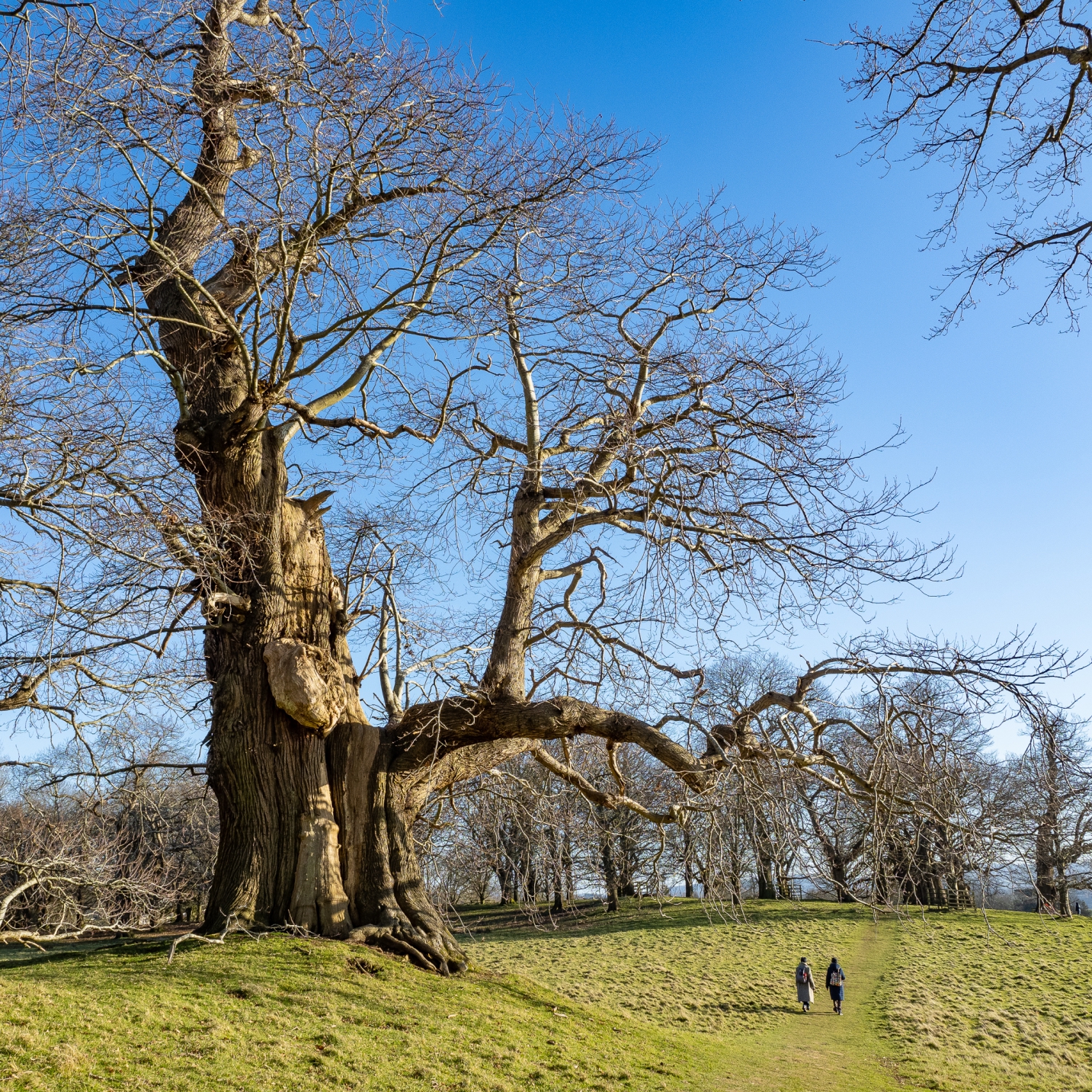
This fine living oak is passed along the way, with signs of cattle gathering underneath its branches for shelter. That’s what causes erosion to the roots, but I don’t know if this is harmful to the tree, or if it’s something they have evolved to cope with over millions of years shared with wild cattle and the like. I have read that the pocking caused by hooves may allow air to reach the roots move effectively than the flat compaction caused by modern human footwear and tyres, etc..
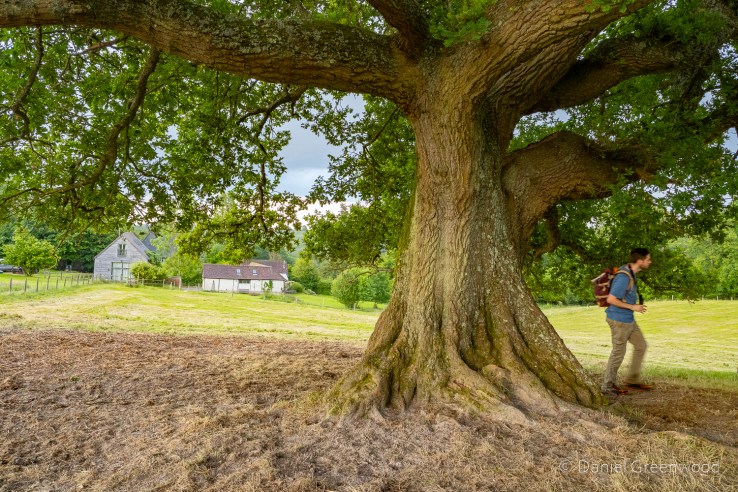

The shelter of the oak is too great to turn down. One oak’s ancient pagan names was ‘dur’, which ‘door’ derives from. This is probably because some oaks had cavities so large you could enter inside them. Also interesting that doors (as per the first image on the post) were once more commonly made from oak.
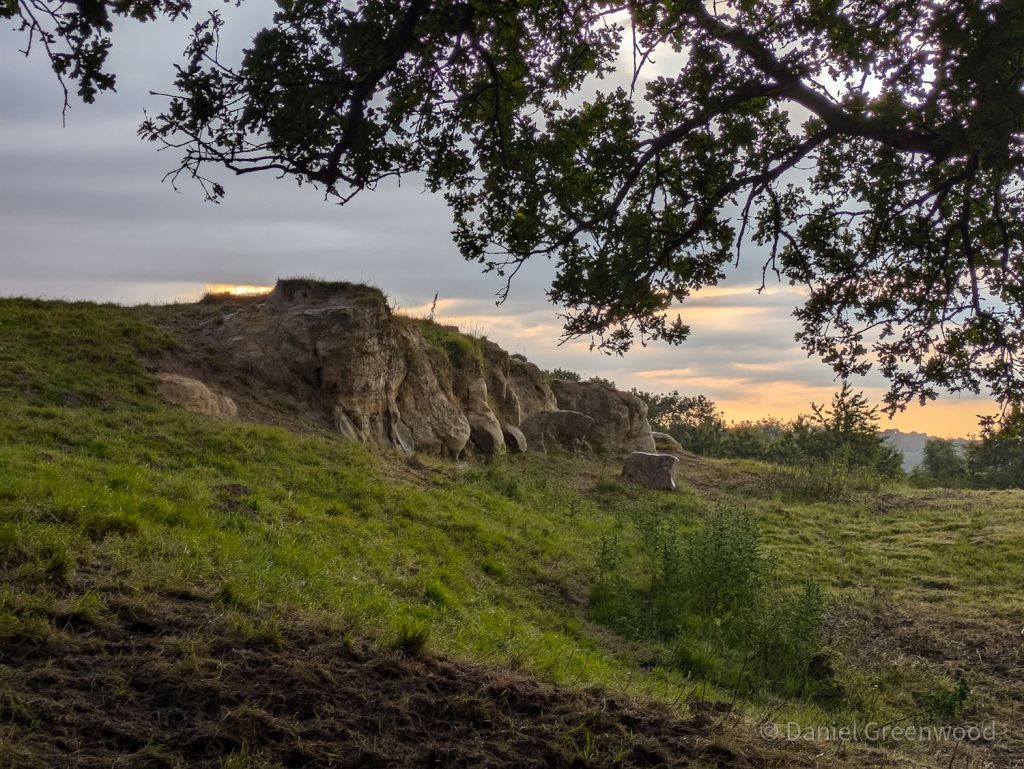

Nearby was an outcrop of rock! That’s exciting here because we don’t really have much in the way of rocky outcrops in the south-east, compared with the Dales, Dartmoor or the Lakes. This is probably the stone used to build Brambletye House, what I presume is a type of sandstone but I’m no geologist. You wonder if this little section has been quarried over the years.
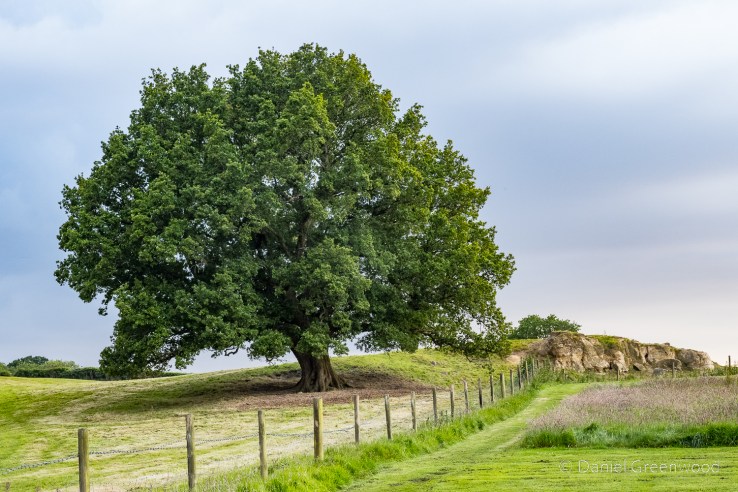

This is our fine oak with the rocky outcrop seen to the other side.
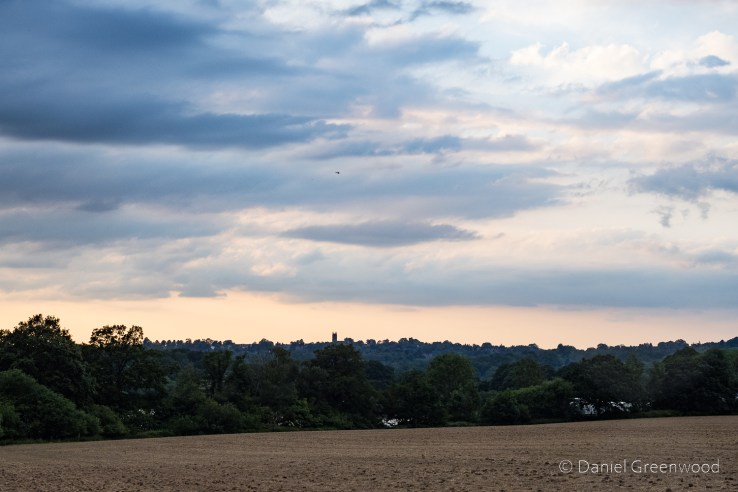

This is a view north towards Weir Wood Reservoir. There’s a church on the horizon and a helicopter high in the sky. Dramatic clouds were developing but we escaped a downpour.

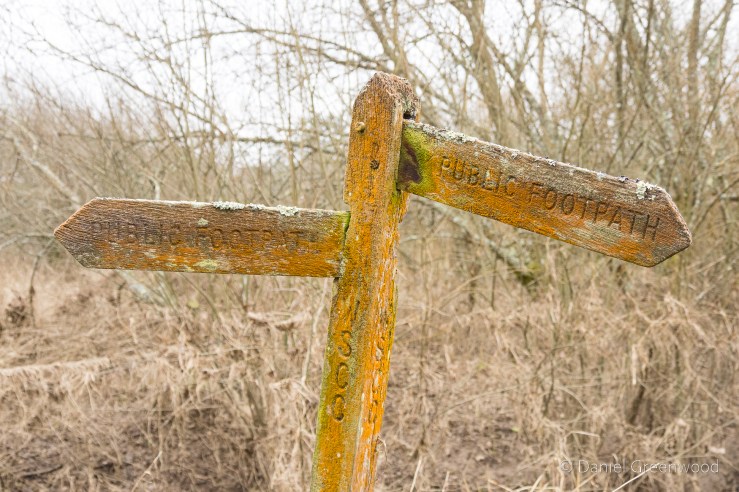
Let’s appreciate this lichen-touched public footpath stone, with its helpful update pointing us in the right direction.
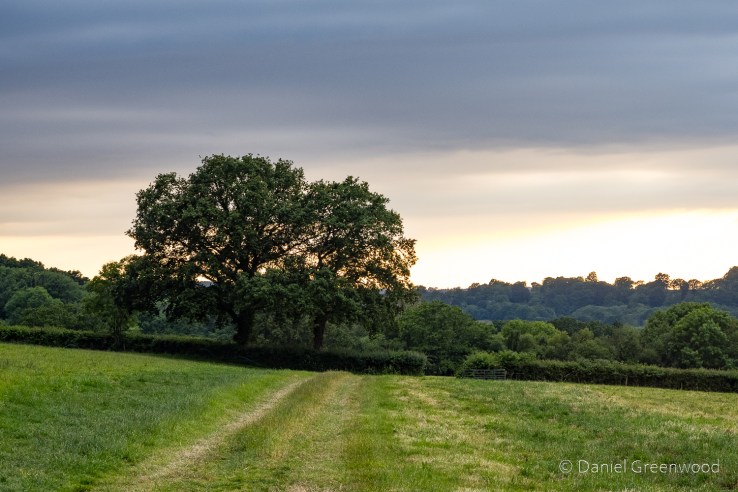

A snapshot of the hedge and oak boundary we passed through on our way to Brambletye.
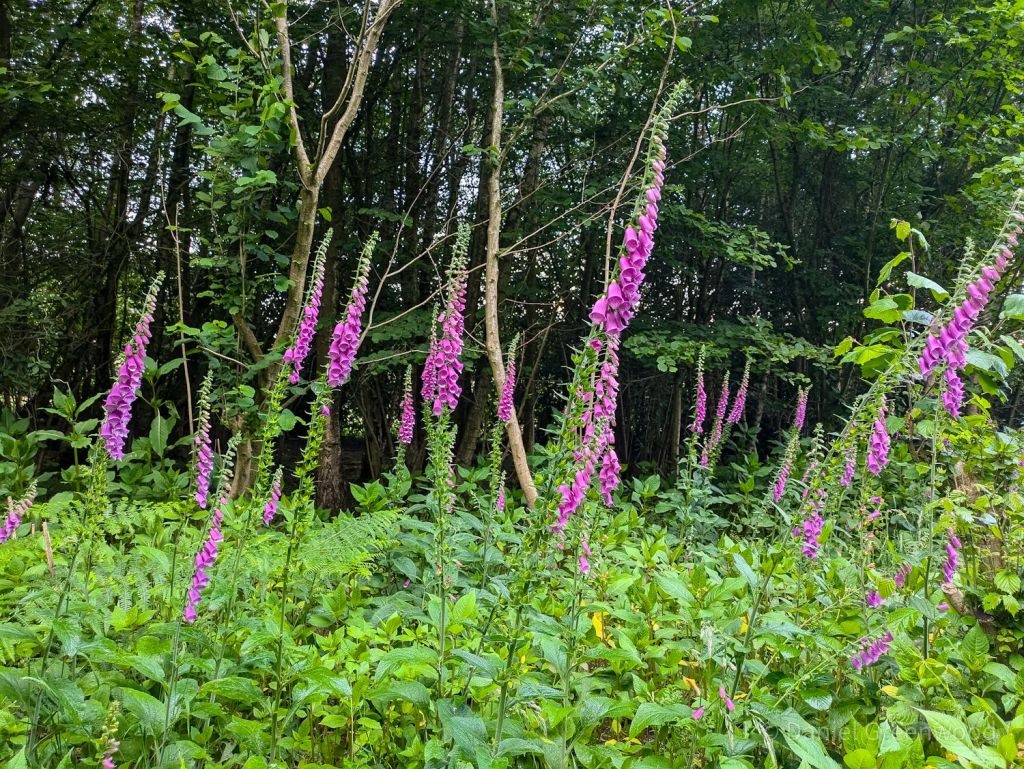

I was taken aback by this magnificent display of foxgloves. June is the peak for this wonderful flower, also a member of the figwort family along with common cow wheat as mentioned earlier!
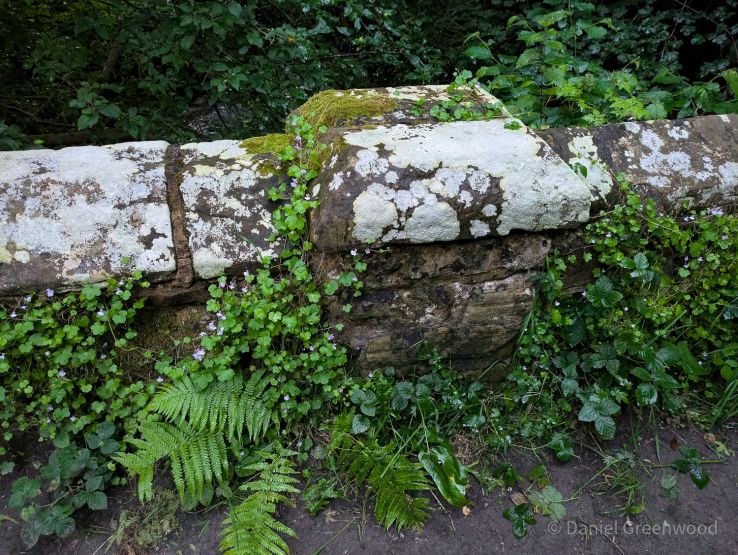

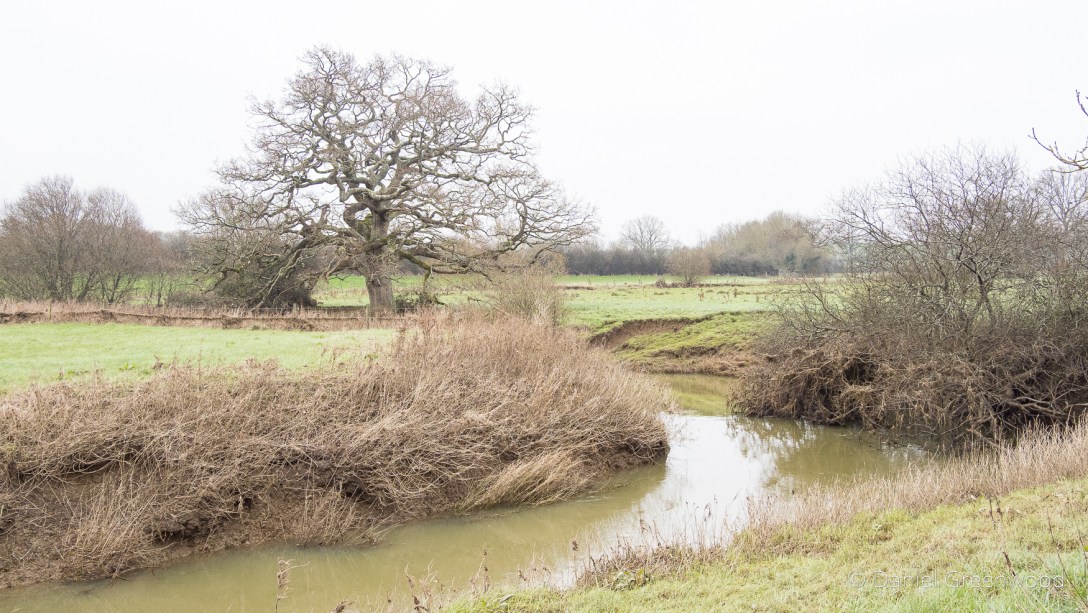
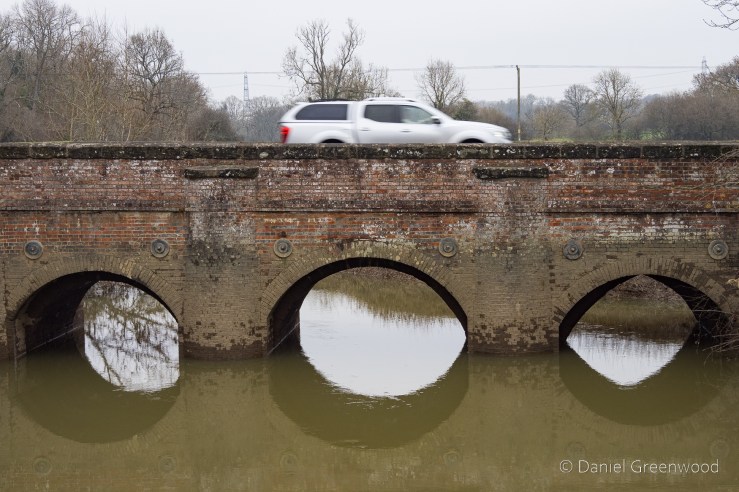
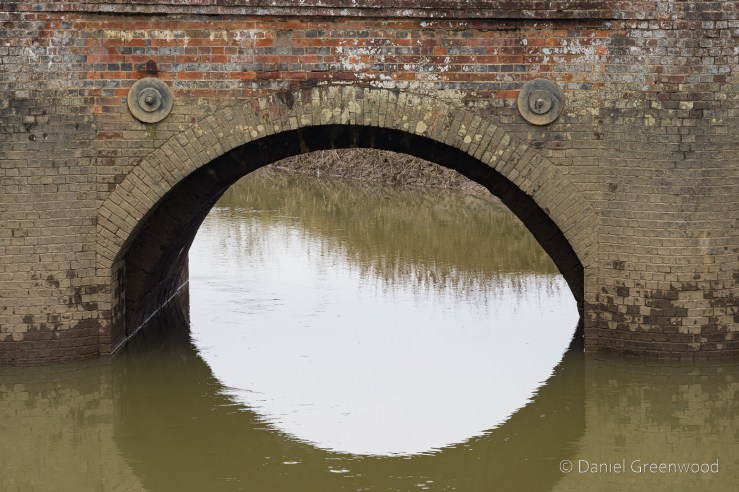
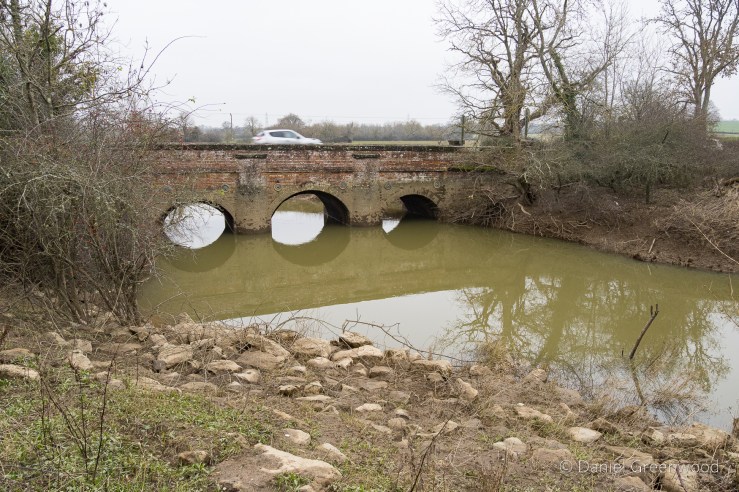
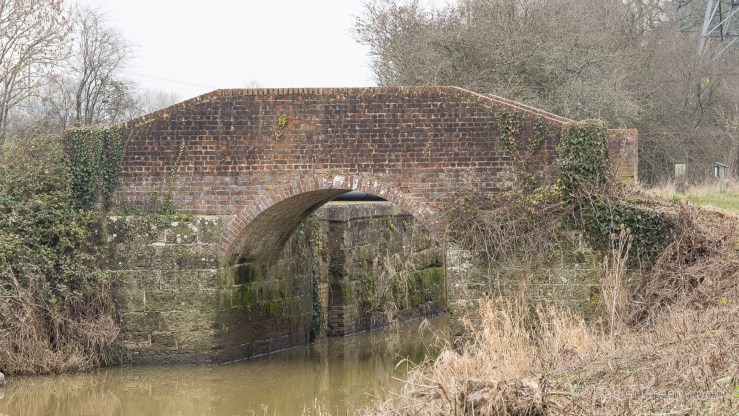
As we neared the famous ruins, we passed over a little stone bridge, what is probably quarried from the same stone seen earlier. It amazes me that this is in fact a bridge over the River Medway, that mighty Kentish river of Dickens and my mate Pete. In fact, by writing this blog I’ve learned that the Medway rises nearby in Turners Hill.
The Medway and its tributaries are known as ‘Wealden Rivers’ – rising from springs across the High Weald where the sand meets impermeable clay.
https://www.southeastriverstrust.org/medway/
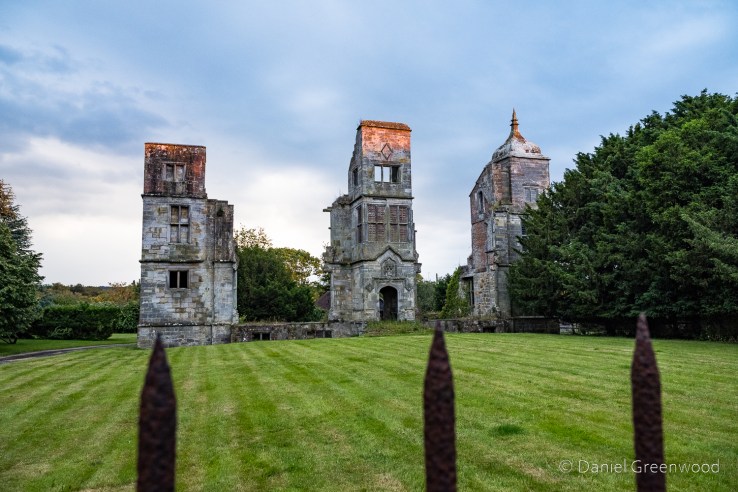

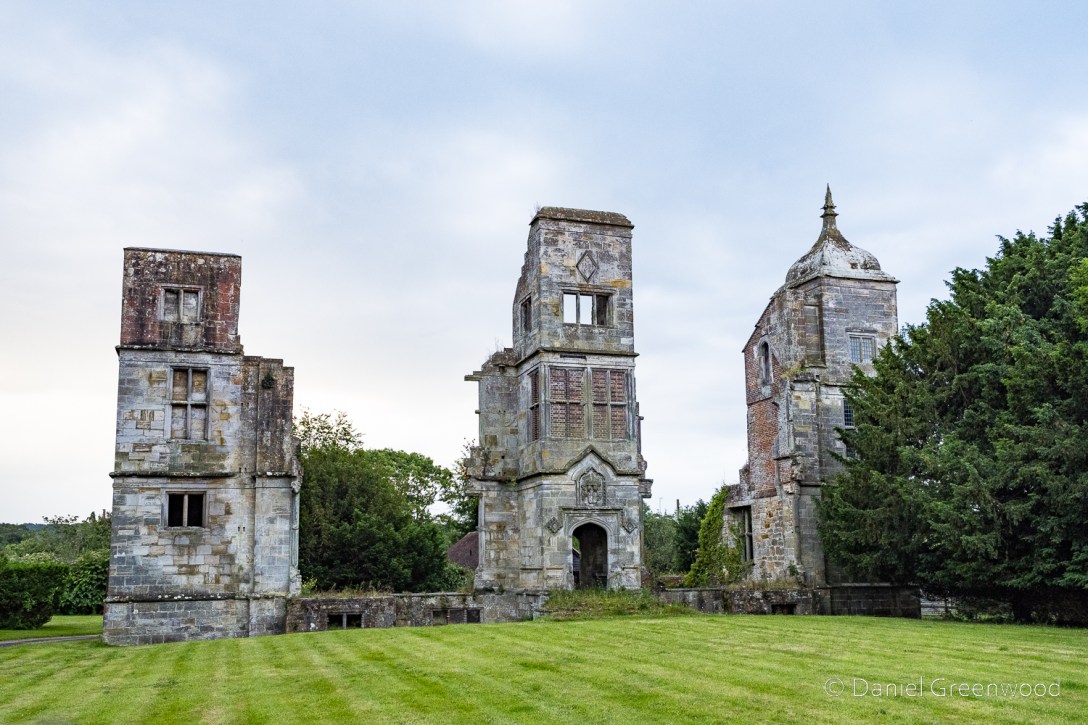
We arrived behind the fence at Brambletye just as the sun began to set, the orange light clipping the tops of each remaining tower. According to Garen Ewing, each tower would have had a minaret similar to that of the western tower. This image is looking south with the towers running east-west.

This old illustration shows two of the towers ivy-clad, and a far more open landscape surrounding them. Now the clump of trees on the western side hides a tennis court, such is the wealth of the current landowner.
It was commissioned by Sir Henry Compton, a prominent landowner and political figure, and would have been one of the most impressive residences in Sussex at the time. However, the Compton family’s time at the manor was short-lived as by the late 17th Century they had left the property – for reasons unknown.
BBC
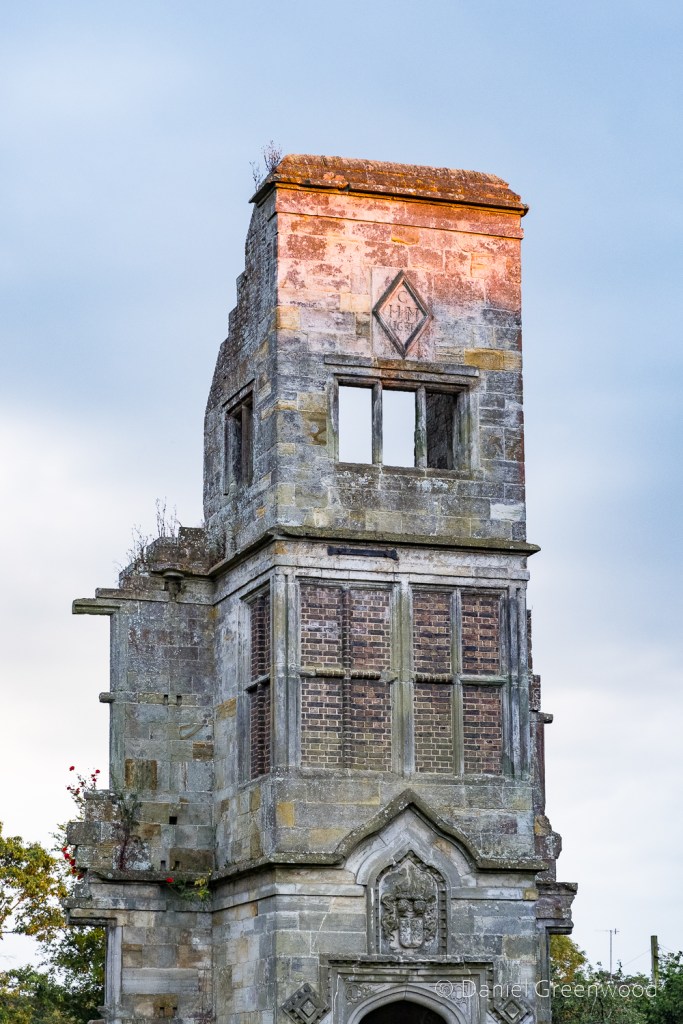

On the central tower you can see the date of Brambletye’s construction, 1681. Also note the bricked-up windows and what I am guessing is the family crest below. I was using my 24-200mm lens so could zoom in for some nice detail.
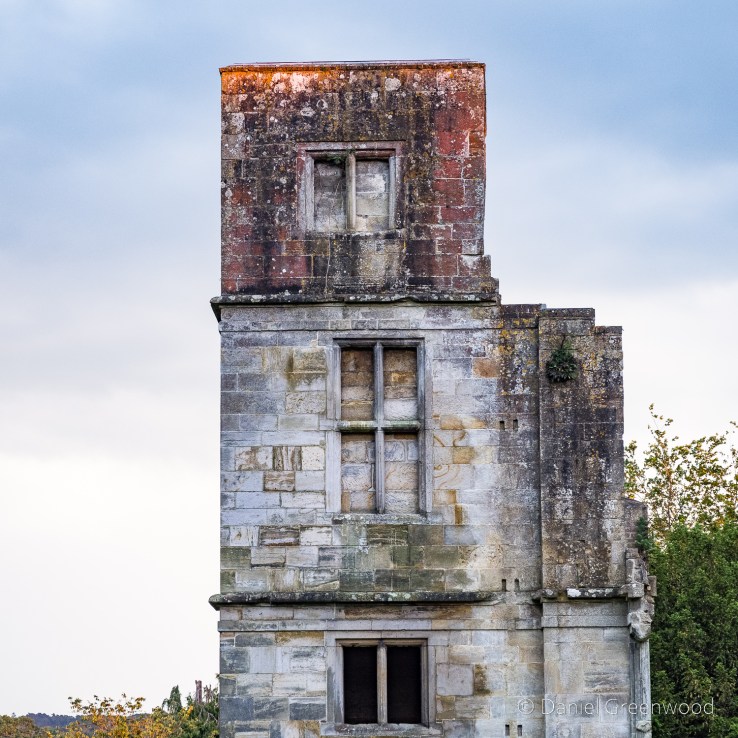

The eastern tower had yet more bricked-up windows – perhaps to avoid the window tax, introduced in 1696 in England, 16 years after Brambletye was built.
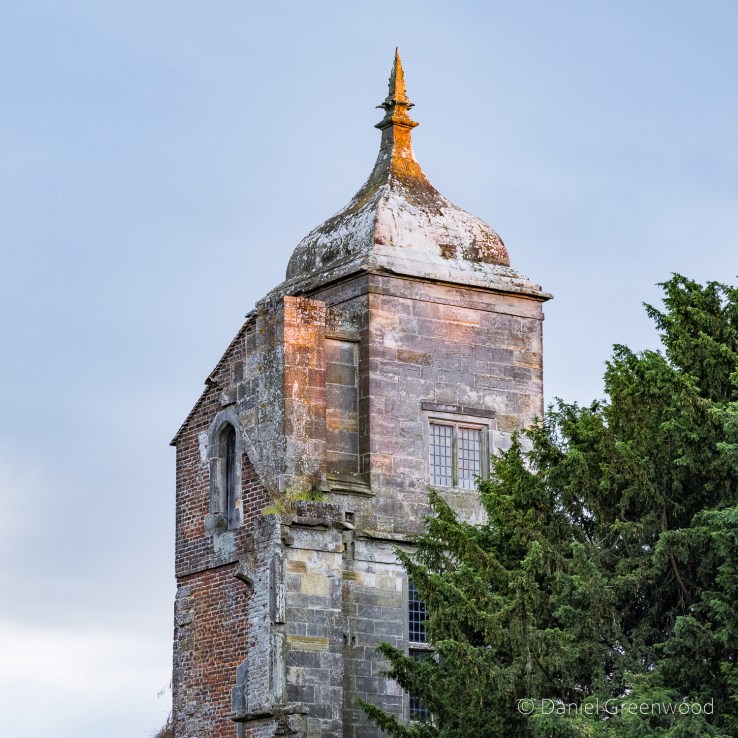

Western tower aglow in the setting sun, an architectural melange.
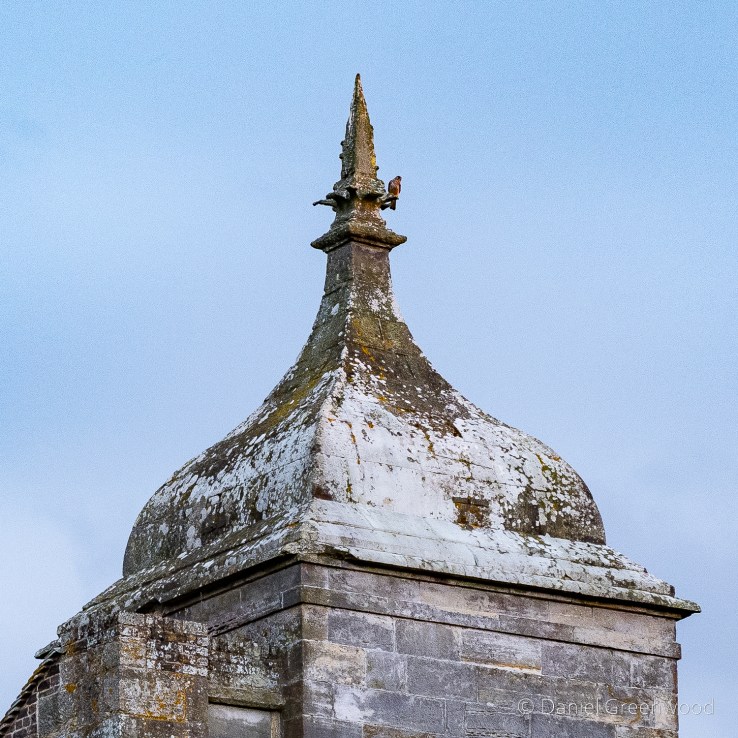

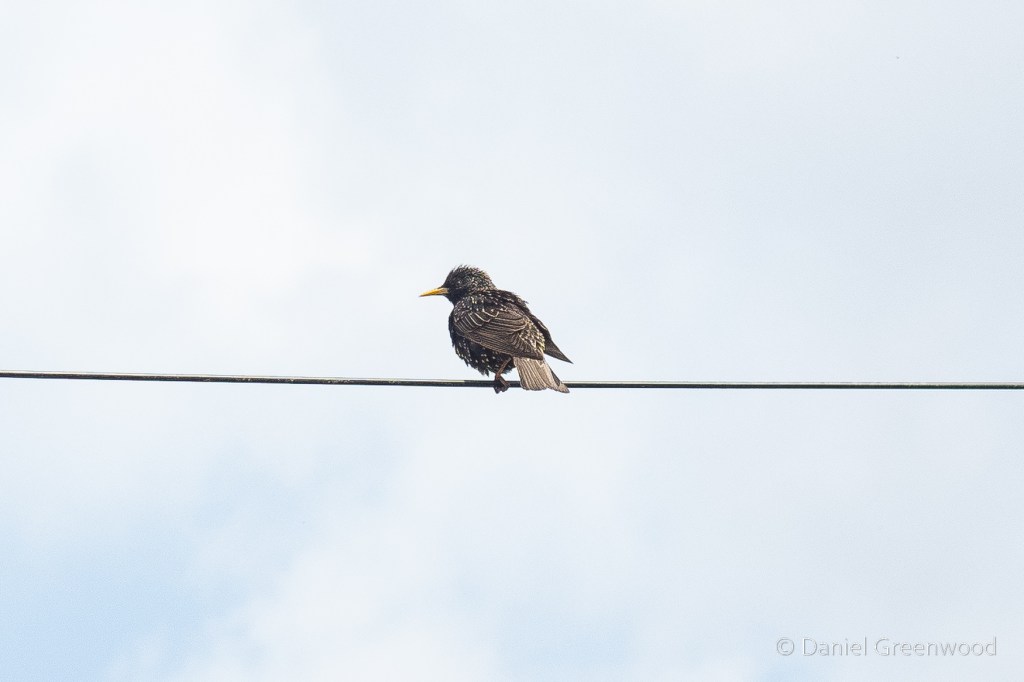
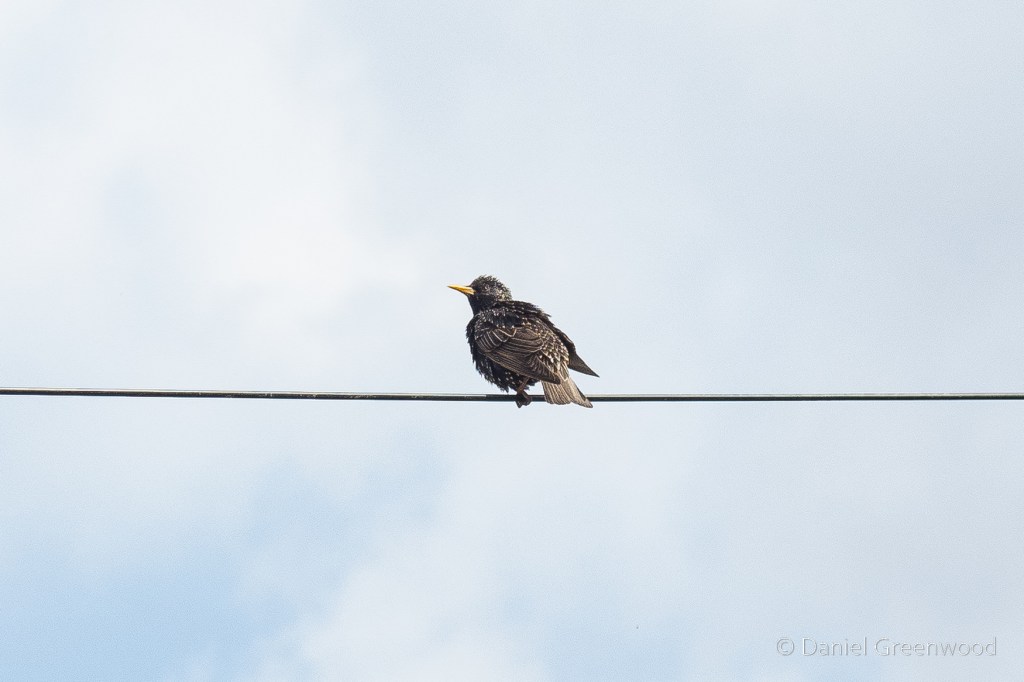
Me and Edwin are both bird nerds, and we were pleased to see a kestrel perched on the only complete tower. Kestrels love habitat like this, and the lack of suitable buildings to nest in has probably contributed to their decline in the UK.
Thanks for reading.